Cloud computing technologies are the backbone of data-driven, application-based, complex ecosystems of products, technologies and services. The Cloud has revolutionized everything. From web hosting and delivery services, to working and playing from home, it has given rise to a multi-billion dollar economy in which many compete for a seat.
With cloud environments businesses have instant access to a broader range of technologies that allows them to quickly innovate or build anything they can imagine. They can also spin-up resources as they need them ranging from infrastructure services to Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, data analytics and much more.
Organizations can deploy technology services globally in a matter of minutes and go from idea to implementation several orders of magnitude faster than ever before. This gives companies room to experiment and test new ideas to differentiate customer experiences and transform their business. By adding machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to applications they can personalize the customers’ journey and improve engagement with the highest efficiency.
Understanding and nativiting this cloud ecosystem as consumers is quite difficult. Apart from industry giants like IMB, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud, the Cloud is a mystery to many. So in this article, we are going to dive deeper and debunk the mystery around the cloud market.
We’ll help you grasp why and how businesses, large and small, are moving to the Cloud, and examine the associated benefits, and the costs involved. We’ll define the different cloud services, name the leading cloud providers and explore how cloud computing is expected to grow in 2021.
The Types of Cloud and Cloud Computing Technologies
Before we go ahead with how the different aspects of the Cloud are expected to evolve, we want to clarify a few main concepts – the variations of cloud computing and cloud solutions.
There are three main types of cloud computing technologies and each has its own unique range of services and cloud providers. These are:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing offer in which the cloud provider supplies on-demand access to computing resources like servers, storage, and network. Within this infrastructure, a company can run their own applications and platforms. Depending on the business’ storage and processing needs, IaaS provides a flexible and scalable hardware resource.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing offer in which the cloud provider grants access to a cloud environment where an organization can develop, manage, and host applications. The platform gives access to a range of tools to support development and testing, and the provider is responsible for the underlying operating systems, infrastructure, security, and backups.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) presents a way of delivering software applications over the web as a service. Instead of installing the application on a local device, companies can use it through the Internet or with an Application Providing Interface (API). The software allows individuals to store and analyze their own data, while the processes of installing, managing, and upgrading the application are handled by the provider.
Each of these service categories gives businesses the option to use public, private or hybrid solutions.
- Public cloud – The provider supplies individuals with access to their data center infrastructure. The maintenance, management, upgrade and security is a responsibility of the provider.
- Private cloud – This is where cloud computing technologies are used exclusively by one business – i.e. an organization hosts its own internet or data center, it has its own ecosystem of server, software, networking or platform resources, which the company owns, manages, updates, upgrades and keeps secure.
- Hybrid cloud – A mix of public and private cloud solutions, where more sensitive information and elements are stored on a private cloud. The interactions between the two services, as well as the security of the data that passes between them are managed within the organisation.
Now that we have these concepts explained, let’s explore how they’ll evolve.
1. Hybrid-Cloud Popularity Is Growing
Choosing the most appropriate cloud solution – public, private or hybrid, for your business can be a challenging task. All three variations have their pros and cons when it comes to performance, flexibility, security and compliance, and as cloud ecosystems are continuously evolving, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
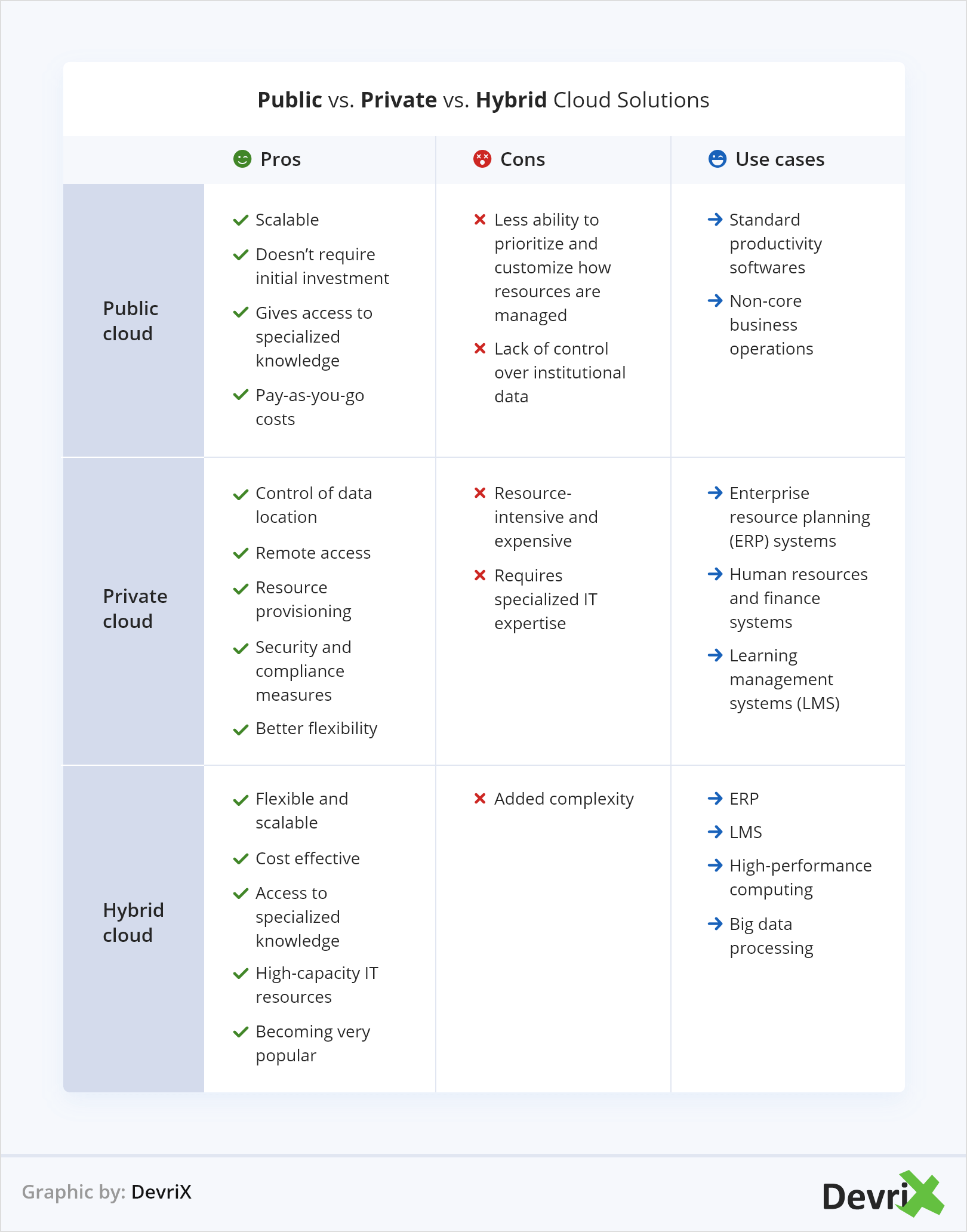
Hybrid-cloud environments are expected to become the preferred choice of many organizations when shifting their operations to the digital space. This cloud solution can help businesses to better meet their own needs and the needs of their clients. It offers greater flexibility when it comes to dealing with sensitive data. And it provides improved security, and more effective compliance with different data protection policies and guides.
According to IBM hybrid-cloud solutions can help businesses address key security challenges by applying new resources and strategies to drive better business outcomes. The many expected as well as unexpected changes in security policies and legislations will require a wider adoption and experimentation of new security technologies, which the hybrid-cloud can assist with. Additionally, with AI becoming more sophisticated and better automated that shift to hybrid can happen much faster and easier.
Hybrid-cloud will also enable a better integration of open-source tools, thus simplifying the skills that developers would need for using and programming this mixed-cloud solution. This way, expertise would be shared much faster into a single, seamless hybrid platform thus shortening the learning curve for both experienced and beginner programmers. What is more, thanks to the power of the hybrid cloud, powerful computing can be brought to your fingertips from any infrastructure, pushing major advancement for privacy and security.
2. Multi-Cloud Environments on the Rise
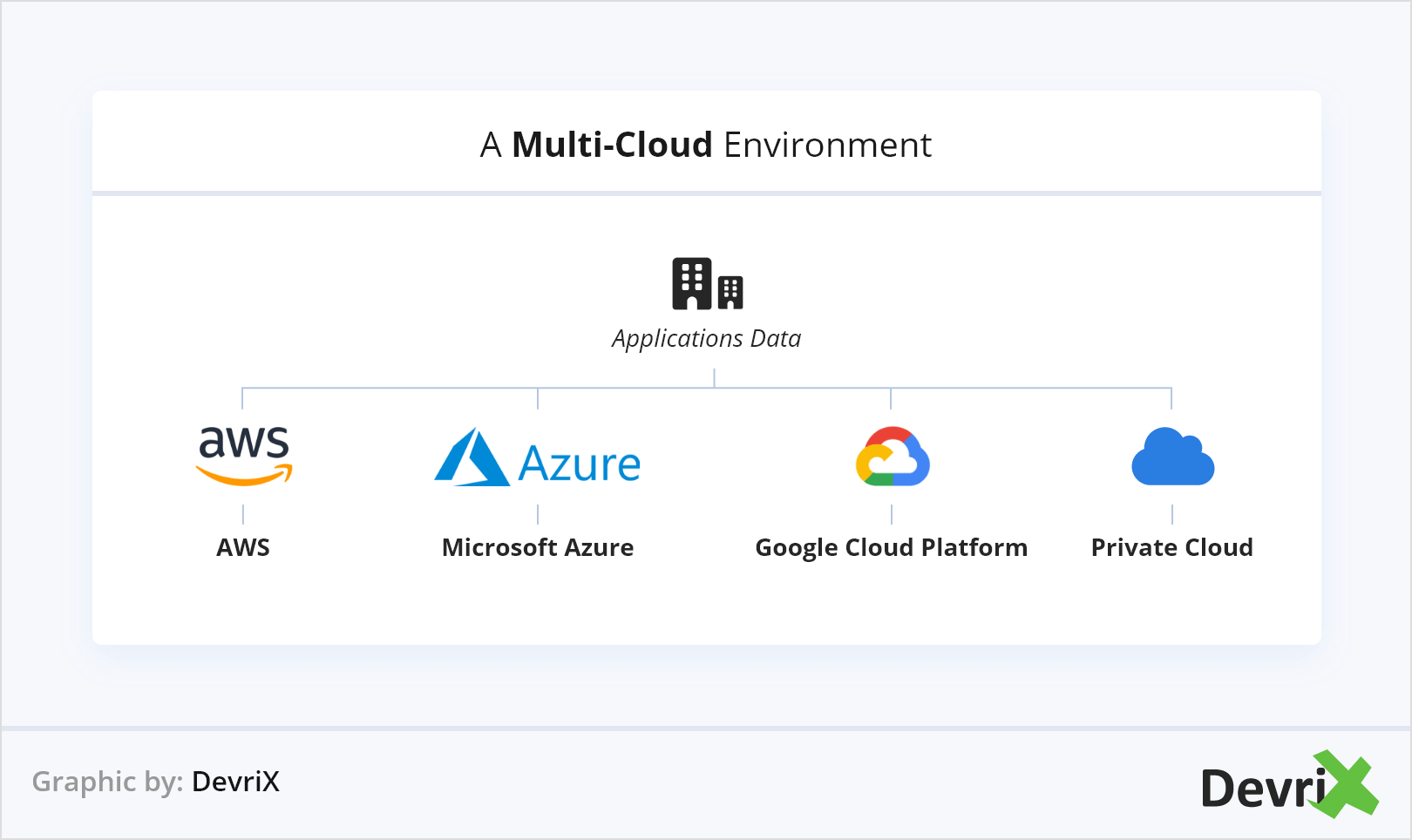
Multi-cloud is a strategy where a company leverages two or more cloud computing platforms to perform various tasks. When in a hybrid-cloud environment there is more than one public service cloud provider combined with private cloud resources, it becomes multi-cloud. If an organization doesn’t want to depend on a single cloud provider it may use resources from several providers to get the best benefits from each unique service.
Generally, multi-cloud describes a strategy that employs several public clouds. This offers up more options to companies to invest in digital transformation with less risk, so that they can optimize ROI, improve security, leverage reliable architecture and be more prepared for the unexpected
With the growing requirements for infrastructure to be deployed across multiple models in 2021 we can expect that organisations will prefer multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud environments, instead of depending only on a single cloud provider. For this, big cloud providers will have to become more open to collaborating with one another to better meet their customer’s needs.
This will also enable organizations to more easily share data with partners in their supply chain, even if they are all working across different applications and data standards. Moreover, we may witness much more innovation from startups as they develop solutions that simplify the operational process between multiple public cloud platforms.
3. AI and ML to Revolutionize Cloud Computing
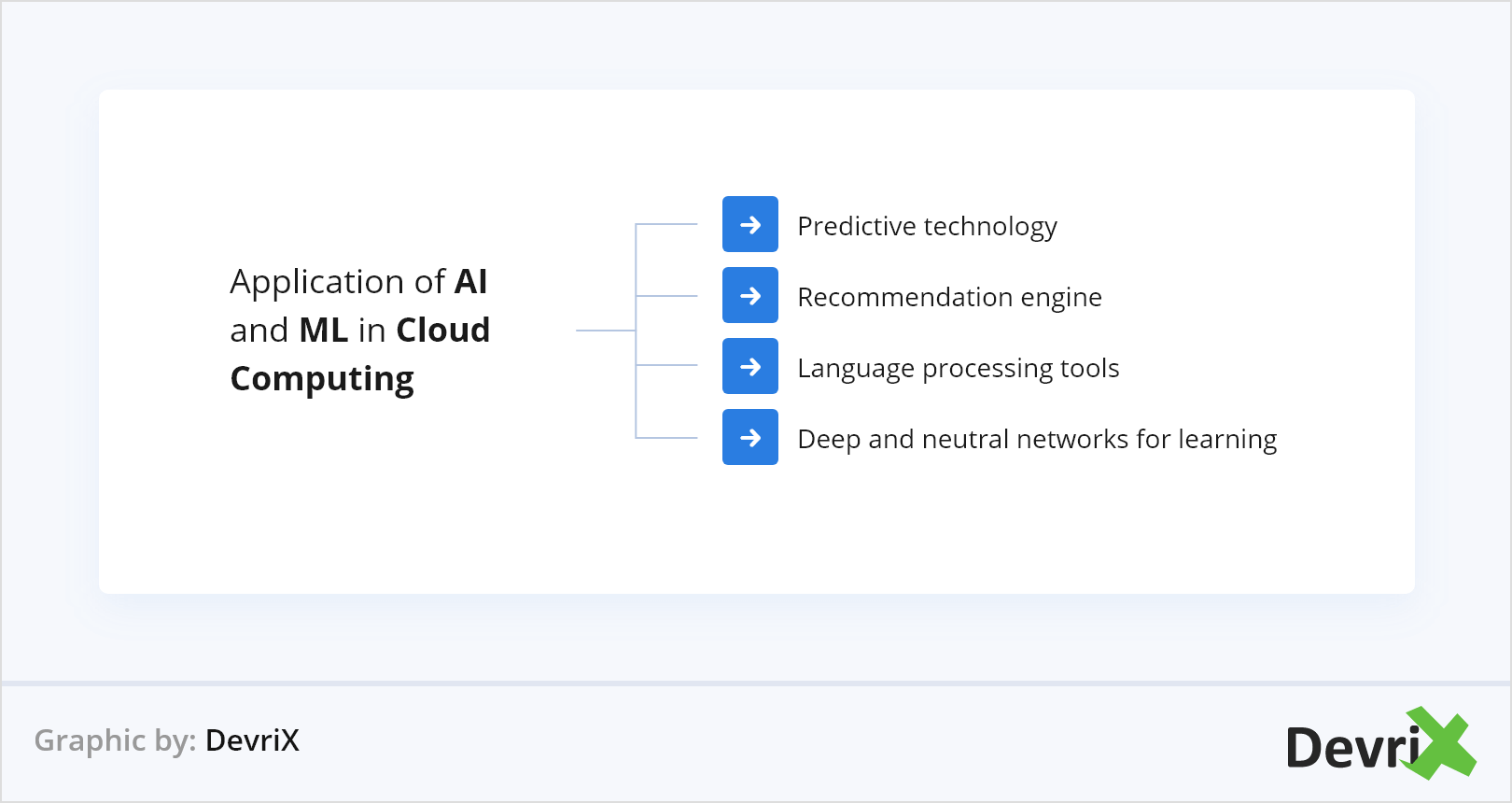
Companies and consumers generate colossal amounts of data every single day – 2.5 quintillion bytes to be exact. With no signs of slowing down, there’s a heavy reliance on cloud solutions for the storage and backup of all this data. And while the Cloud is able to accommodate so much information, the spread that it’s generated is nearly impossible to manage manually. However, with the help of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), the Cloud can be significantly elevated.
On the one hand, AI is a key component of enabling technology to adapt to customer needs and thanks to cloud technologies these can be more easily deployed and used by organisations. Many SaaS businesses already use AI in various ways – predictive technology, machine learning, recommendation engines, language processing tools and so on.
On the other hand, ML is a key combination of algorithms thanks to which AI can learn from overtime and get better at it over time. It can perform cognitive processes and predict outcomes, thus accelerating the rate of innovation in almost any industry.
When used with cloud computing technologies and solutions, AI and ML can bring valuable improvements to organizations. The Cloud makes it easy for businesses to measure and test ML capabilities at the same time as projects go into production. It offers access to intellectual features without the need for advanced skills in machine learning theory, AI or data science.
What is more, ML and AI offer reliable scaling, better automation, and access to bigger and better data. With clouds, a company’s growth is not limited to in-house resources or expertises and products and services can be automated with less strain on their human teams.
4. Virtual Cloud Desktops to Become a New Norm
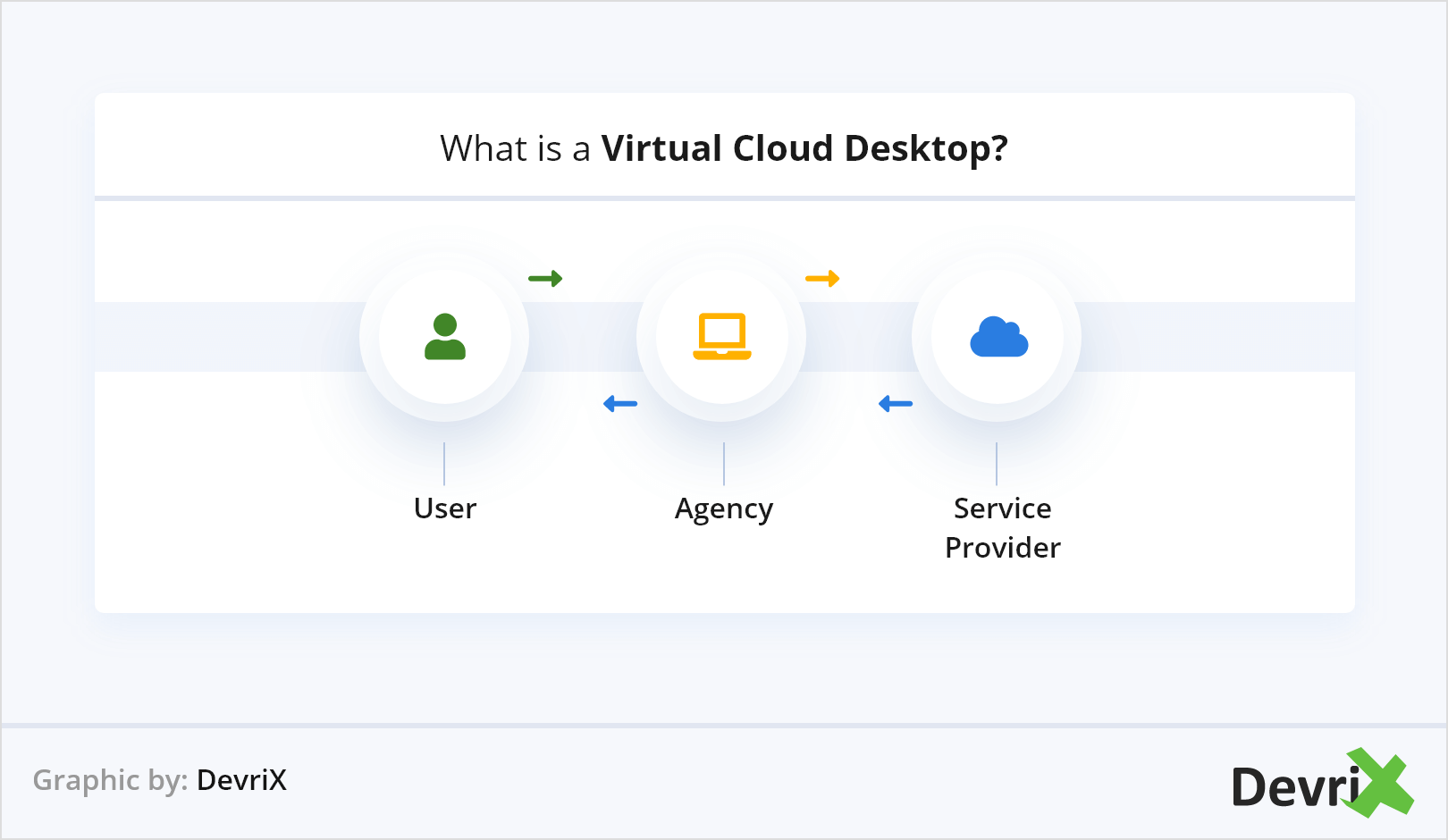
With the growth of remote jobs, comes the need for more functional and cost efficient ways to manage employees’ work. This is where visual desktops come to the rescue.
Virtual cloud desktops are where the entire environment of a workstation is delivered as a managed cloud service to a laptop or desktop screen. This can bring significant advantages to organizations including by-the-hour subscriptions for the time employees spend working on their devices, thus reducing the cost of hardware updates and the need to dispose of old technology.
This model, also known as Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS), is already offered by Amazon, Microsoft, IMB and Google. By ensuring everyone is using up-to-date, synchronized technology adopting DaaS can help companies increase efficiency across teams and business units. It’s also beneficial for security since all devices can be managed in a centralized way, rather than having to keep track of everyone on the network to ensure they’re following best practices.
Additionally, virtual desktops offer much more flexibility when company teams shrink or grow. If employees join or leave a company, the cost of this service is adjusted according to how the number of hours spent using the platform.
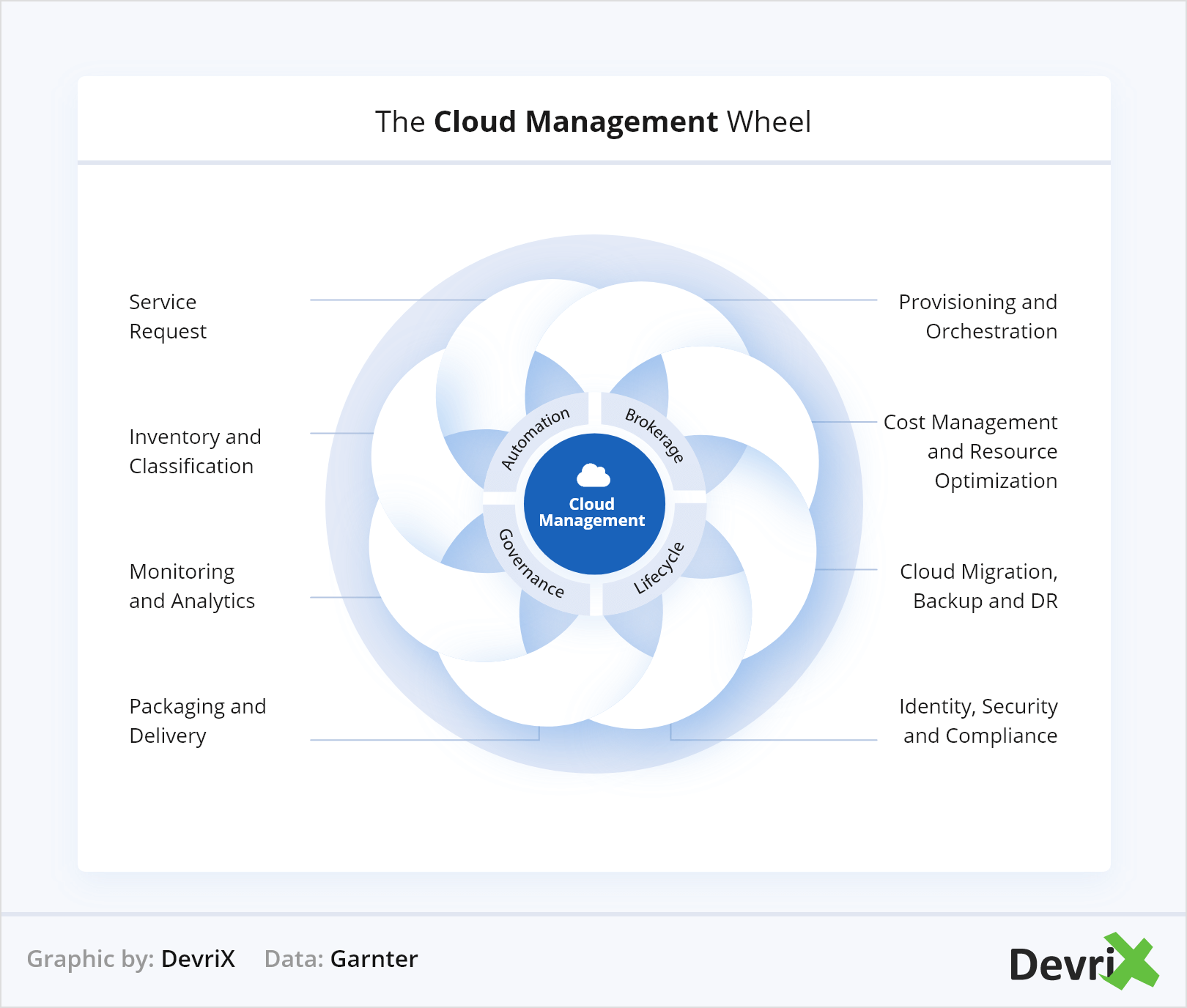
5. Increased Need for Better Cloud Management
Moving workloads to the cloud has greatly improved some operational efficiencies and collaboration, but it has also proved to be costly, especially when there are gaps in employees’ skill sets.
It’s important that vendors of cloud computing technologies as well as companies that use them adopt cloud management practices so that the benefits are clear. Furthermore, due to the complexity that cloud computing has, many users don’t have the skills sets to use cloud infrastructure efficiently.
What companies can do to bridge this skills gap is conduct internal training, seminars and workshops and design appropriate onboarding processes. Additionally, they can take advantage of the benefits of knowledge transfer that hybrid and multi-cloud solutions propose and use them for faster and easier access to learning materials.
Conclusion
The world of cloud computing technologies is anything but simple. There are complex ecosystems and much learning involved. However, in 2021 the transferring of this knowledge will become accessible to anyone, regardless of their skillset, to embark on a continuous learning journey at a rate never seen before.
By revolutionizing basically every aspect of business performance, the Cloud has accelerated innovation at a remarkable rate. Organizations can become more agile and flexible, scale faster without putting their resources at risk, and save costs, all while deploying globally in minutes.