Product development and service design are what tailors your services and products to end-users needs, pain points, and requirements. As we look through the most successful projects launched in recent years, personalization is steadily becoming a determining factor for success. Examples are all around us, from Spotify allowing you to discover music daily, based on what you’re currently listening to, to Facebook that moves your social life to a digital newsfeed.
To successfully implement an effective process of product development or service design you need to approach the initiatives the right way, meaning to gather the required data, analyze it carefully, and use it as a user-centric compass, leading the way for your business development.
The Process of Developing Products and Designing Services

Both service design and product development are not one-time projects that redevelop your business. They’re constant processes that follow a strict cycle with multiple stages:
- Conception – Ideation, brainstorming, user feedback for gathering of initial ideas and planning the development process
- Development – At this stage, the service or product is developed as a prototype and polished with the help of subject matter experts and test groups.
- Launch – The product or service is being launched or implemented, user reactions to the new product or service need to be closely monitored
- Sustain – The product or service is already launched, users’ feedback is closely monitored, and the product or service is constantly being updated based on consumers’ needs and preferences.
- Discontinue – The product or service is being discontinued to introduce new products or services to the audience.
Most of these stages are connected to creating plans, implementing processes, automating work, and solving problems, but there are two crucial steps that you need to gather data for, that will give you the ideas of what you need to include in your plan, what processes to implement, and what problems to address. The stages that required close monitoring of users’ feedback are:
- Before the Conception – Shape your product or service according to customers’ needs, be able to spot market opportunities, mark users’ problems, and leverage them.
- After the Launch – Check whether the initial research and assumptions were correct and whether the reach and sales go according to the business plan and to provide you with insights into what needs to be changed if the users are not responding as predicted.
Buyer Personas
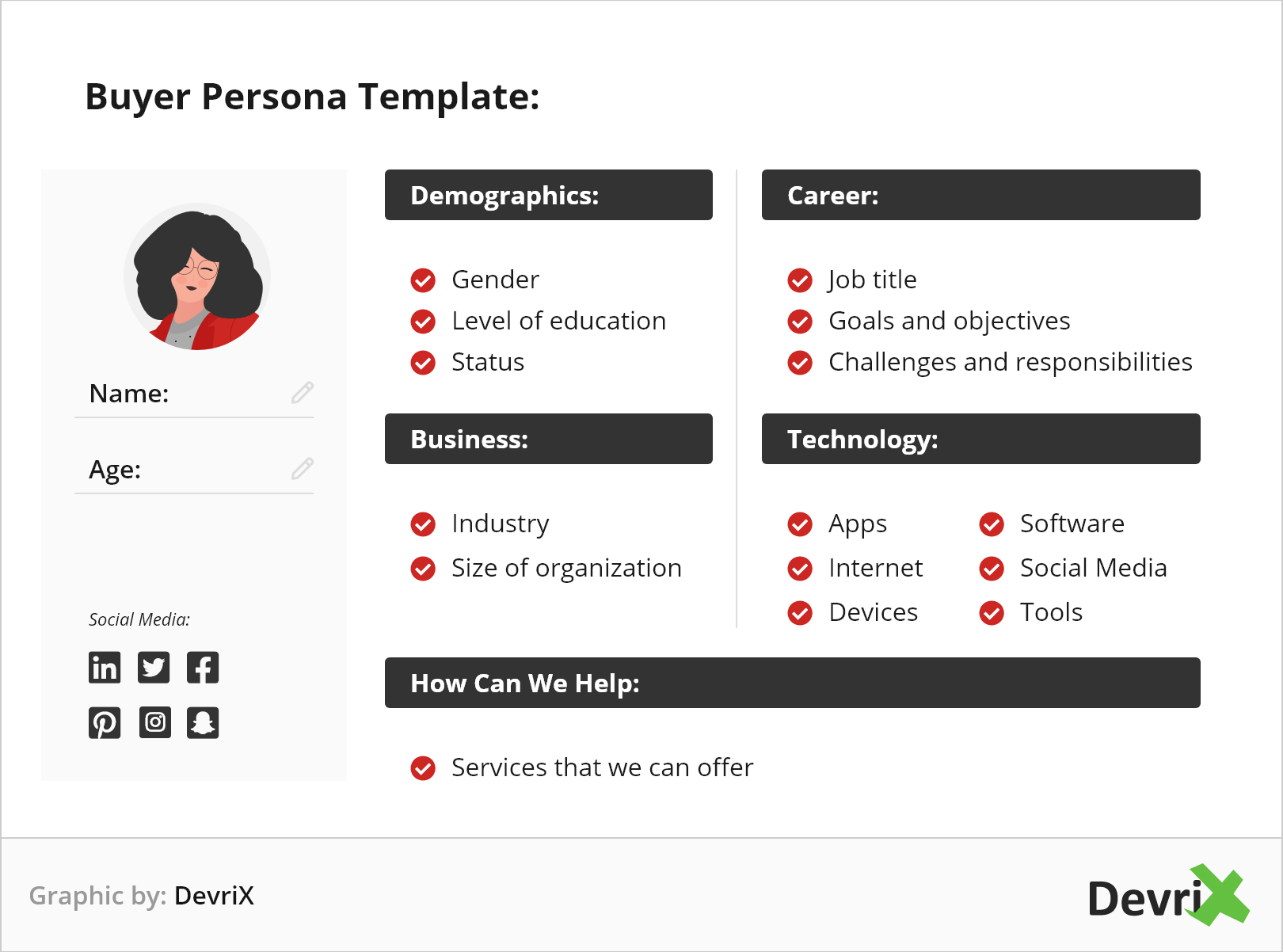
A buyer persona is a psychographic profile of your ideal customers, displaying their interests, goals, channels used, pain points, challenges, behaviors, and demographics in an easy-to-gasp, infographic way. This information will help you get powerful insights into customers’ requirements and pain points and will help personalize your service or product to fit their needs.
The best way to collect such data is through social media listening, and the user or partner surveys. Having an in-depth psychographic profile of your ideal customer could help you slash through the competition finding a unique audience or a unique way to engage it.
Competitor Research

Where to find the data for competitor research via Best Engaging Communities
Competitors analysis or research focuses on the channels, content, products, services, posting schedules, and overall marketing efforts and business model of competitors. It’s used to help you understand the market and industry-wide trends, see what current customers of your segment are engaged with, and get accessible ideas you can implement to achieve tangible results.
Furthermore, competitive research helps polish the product or service and come up with competitive advantages, value proposition, and unique selling points.
The best way to approach this research is to look for information on competitors’ websites, social media, and leading forums. This will give you an understanding of what brands are promoting, and what users think, helping you form a coherent view of the market.
Customer Surveys
Although there are two crucial stages (before Conception and after Launch) when customer feedback has to be collected to set your product development or service design in the right direction, regularly gathering such data will help you to:
- Get information about what you need to develop further or polish
- Know what customers like about your product/service and incorporate it into your value proposition or gather testimonials
- Find your competitive advantages or disadvantages
- React to market changes promptly
One of the best practices that will help you collect users’ feedback proactively is to survey new customers shortly after their first experiences with the product or service. The goal of this research is to understand how appealing the product or service is and for what audiences?
It also looks at the average time to get used to it, and how easy it is to grow your audience with your current marketing efforts and business model.
Users love when a company listens to their feedback and acts accordingly. Such efforts increase retention rates and customers’ loyalty, turning your audience into a community. This is why it’s essential to provide easy access for active, non-new users to a survey gathering data for peers well-acquainted with your product.
The best practices when it comes to the surveys themselves is to keep it short and sweet. 10-15 multiple-choice-questions are ideal because this guarantees more users will participate in the customer survey. This way the feedback will be more valuable because of the easy-to-understand-and-answer questions.
Leave an additional section for further comments to get a deeper insight into consumers, their needs and behaviors. Use everyday vocabulary to make the customer survey easy to answer and assure question flow is understandable through target-market-pilot-tests.

Exemplary Questions to Add in a Customer Survey:
- How many hours a week/day do you use the product/service?
- Did you evaluate other similar products/services before selecting this once?
- Which products/services did you evaluate?
- What will make you use the product/service for more hours a week/day? (you can list more than a single thing)
- Do you find the product/service easy-to-use?
Your goal is to gather enough quality data to drive up your product development or service design. To do this, regularity is key. Use regular, more detailed small surveys for new customers and quarterly large-scale surveys with clients.
Sales Channel Survey
The main challenge for most marketers is to make the sales team respond to your survey in the first place. Usually, sales teams have their targets and are rushing towards them like a war machine, but they see little value in sales channel surveys because surveys make their work much more cumbersome.
An easy fix for this problem is to explain that the collected information will be used for product development or service design. It might also be helpful to point out that such research could help you get significant insights into customers’ needs or behavior that will help drive up the sales.
The sales channel survey is extremely important because it shows how easy or difficult your products or services are to sell.
Exemplary Questions to Add in a Sales Channel Survey:
- Which products/services are the easiest/most difficult to sell? Why?
- What will make it easier for you to sell the product/service?
- What are the most important features the product/service is currently lacking?
- Who do you see as our major competitor(s) for the specific product?
- Do you have a strategy to sell against this competitor?
Customer Visits

Customer visits are probably the best way to understand the acceptance of your product or service. They’re also useful for building a strong community around your brand as such initiatives make the client feel meaningful and appreciated.
The customer visit is a two-way dialog session on which the company (you) presents its future development plans to customers. These meetings are used to gather feedback from current users, to start educating your audience on your plans, and to sell your products or services.
Exemplary Questions to Ask During a Customer Visit:
- What are your needs and requirements for this type of product/service?
- Do our products/services meet these requirements? Where are they deficient?
- What do you like best considering the presented product/service?
- Are you well acquainted with competitor products/services? How are these products/services better/worse than ours?
- What is your company direction regarding the use of our product/service?
- Are you evaluating other similar products or services? Which ones?
User Testing
Another practical way to get the engineering team introduced to consumers’ needs and behavior is to invite people and let them use the new product or service you’re developing. Such initiatives are extremely important because they give validation of the demand or design and assesses the ease-of-usage.
User testing could help you get significant insights into customer behaviors and general knowledge, figure out whether you have to educate your audience regarding the product or service and find what could be designed better regarding the user and information experience.
From Feedback to Ideation
One of the best practices you can implement is to gather customers’ ideas through a single, easily-accessible place. This will help you have a coherent view of future development needs.
When it comes to building a platform where users could give their ideas, two crucial things need to be implemented. First, users’ input should be easy-to-fill-out to ensure more customers are going to participate. Second, all ideas should be grouped into larger themes to be able to make a coherent development strategy rather than partial updates being conducted one at a time. Themes help you organize your process and give all peers in it an easy-to-understand, thorough view of users’ problems and ideas.
Keep in mind that some users are extremely vocal. When you’re gathering feedback and ideas for product development or service design, it’s important to ensure that not the loudest but the most viable clients are heard. This requires a specific methodology implemented to prioritize ideas either based on who they’re coming from or through a voting mechanism allowing all users to cast their votes for certain ideas.
Collecting feedback for ideation purposes is important in product development and service design because this initiative helps drive the development process even more towards customer-centricity and personalization.
Data That Drive Product Development and Service Design
Gathering feedback and data about customers, competitors, and the market are extremely important when you’re making long-term, complex strategies. Our job as marketers is not to launch the perfect campaign for the best product because such things do not exist in real life.
Our job is to understand the market and the consumer, try different approaches, gather data about consumers’ reactions to each of them, analyze, and polish the product or service day by day. Our job is to learn and understand how to meet the ever-changing requirements of customers, continue growing our audience and reshaping the world bit by bit.




