Switching from Universal Analytics (UA) to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) might sound a bit complicated, but don’t worry, it’s actually understandable if you start with the basics and build from there.
GA4 brings significant changes, and while some familiar features may seem missing, it introduces a new data model, cross-device tracking, refined session definitions, new metrics, improved analysis, better attribution model, and substantial machine learning capabilities.
To make the process easier for you, we’re here to compare GA4 vs. Universal Analytics, and explain all the key changes and new developments as clearly as possible. Keep reading because we are covering everything you need to know about:
- GA4 vs. Universal Analytics: changes and differences.
- How machine learning is shaping the future of Web Analytics in a cookie-less world.
Readers also enjoy: 6 All-Inclusive Website Analysis Tools You Should Know About – DevriX
What Changes with Google Analytics 4
The main purpose of both Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Universal Analytics (UA) is to help you understand how users behave on your website, but the two have some key differences.
A New Data Model
Google Analytics is a data collection tool. However, in the case of Google Analytics 4 vs. Universal Analytics, GA4 employs a new data model to gather information.
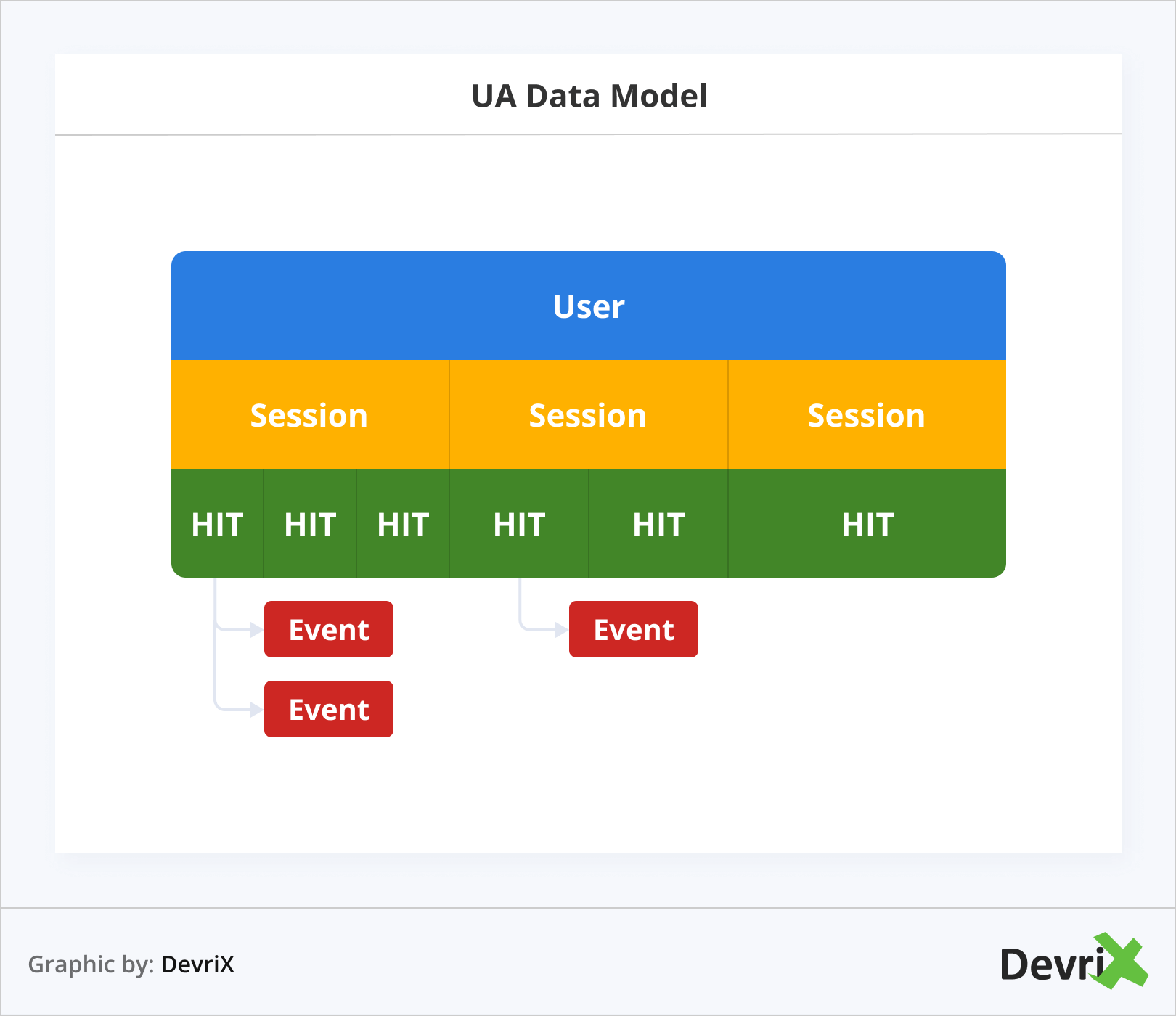
- Universal Analytics uses a layered User-Session-Hit data model.
Universal Analytics is based on its layered User-Session-Hit model. The first layer is the user or more specifically the browser identified by the GA cookie. The second layer is the sessions that each user had. The third one is the “hits” or all the actions on the website such as clicks or pageviews. This model is functioning well, but attempting to conduct deeper analysis or apply machine learning to the raw data could pose a challenge.
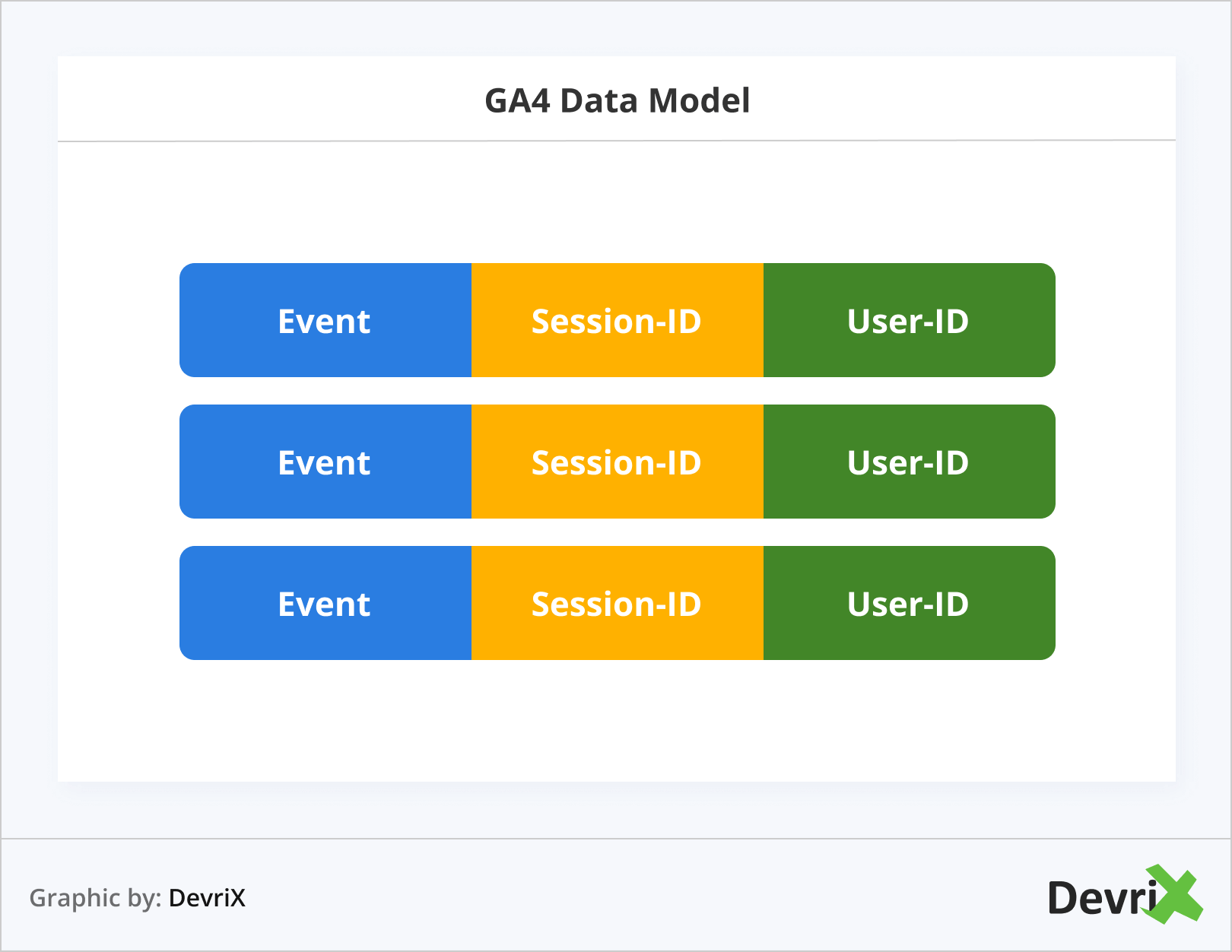
- GA4 has a flat, event-based data model.
In GA4 everything that happens on the website is considered an event and it is “flat”, rather than hierarchical. This flat structure is important for machine learning. That doesn’t mean that there are no more sessions or users. Each event in GA4 has parameters for session ID and user ID, connecting them to specific sessions or users.
Cross-Device Tracking
![]()
GA4 is on its way to overcoming one of the biggest challenges in web analysis – cross-device tracking. In UA, the user ID identifies the browser instead of the person. This is still a default in GA4 but the biggest change is that if your website offers a user login, you can use its login ID instead of default user ID. When a user logs in on your website on two devices, you will only be counting one user now instead of two. This allows you to keep track of them across multiple devices.
Readers also enjoy: Quality Score Optimization: How to Boost Your Google Ads Results- DevriX
Improved Sessions
GA4 improves the concept of a session.
- In UA, a session breaks when the traffic source changes or at midnight.
- In GA4, the session continues in both cases, assigning events to various origins within the same session.
Here is an example: Imagine you’re looking for project management software. After Googling and checking different options, you realize you need a cloud-based solution. Clicking on a sponsored ad, you’re taken to the software provider’s website. In Universal Analytics, they’d see two sessions (organic and paid), but in GA4, only one session is counted. GA4 attributes the first event to organic search and subsequent events to paid advertising.
When it comes to session breaks at midnight, Universal Analytics creates new sessions, while GA4 maintains the same session ID, ensuring session counts reflect real numbers.
Old Metrics, New Metrics
By replacing well-known metrics in UA, GA4 introduces a new set of metrics that dive deeper into user behavior and engagement.
- Some metrics in UA are not available in GA4.
Say goodbye to the unique page view and bounce rate. These were among the favorite metrics – unique page views are the number of individual sessions during which a specific page was viewed at least once. Bounce rate is the percentage of single-page sessions, where users leave without interacting further with the site. Тhey are no more. Session duration is also missing. - GA4 introduces the engagement rate metric.
The new engagement rate metric is the biggest change. It is the opposite of the bounce rate. A session is considered engaged when a user visits two pages, and starts a conversion event, or keeps the website or app open and in focus for more than 10 seconds. GA4 also brings in a fresh metric called “engagement time” that shifts the focus away from bounce rate. It encourages analyzing user behavior and fostering engagement on the website as key indicators of success.
Improved Attribution Model
GA4 introduces a new and improved attribution model that accurately tracks and assigns conversions to different touchpoints along the customer journey.
- UA uses the Last Non-Direct Click Model.
The Last Non-Direct Click model means that the last channel in a user’s conversion journey receives all the credit for the conversion, while the other channels that assisted in acquiring the user receive none. - GA4 uses a Data-Driven Attribution Model.
It is an event-based data collection model that allows applying any predefined data model, with the default being the data-driven attribution model. The new model considers time to conversion, device type, number of ad interactions, and order of ad interactions. GA4 applies the chosen attribution model to conversion numbers in all reports.
Data Retention
One important change in GA4 is the user data retention period, which refers to how long Google keeps user interaction data. In UA, the default option was “unlimited” data retention. However, in GA4, the maximum duration you can retain events and user data, including conversions, is 14 months.
This could cause problems with scientists anand education marketers who rely on year-over-year comparisons. However, integrating GA4 with tools like BigQuery and utilizing reporting tools such as Google Data Studio can help overcome this challenge
The data retention restriction does not apply to standard aggregated reports, where you receive reports based on sampled data.

Readers also enjoy: How to Use Artificial Intelligence in eCommerce – DevriX
The Power of Machine Learning in a Cookie-Less World
Machine Learning comes in to fill out the data gaps and to provide predictions in a cookie-less and privacy-conscious world. ML feeds data into AI algorithms predicting the future behavior of your users and introducing exciting ML-based features.
The combination of GA4’s machine learning and behavior modeling empowers businesses to make better decisions and optimize their marketing strategies based on a deeper understanding of user behavior.
Advanced Insights
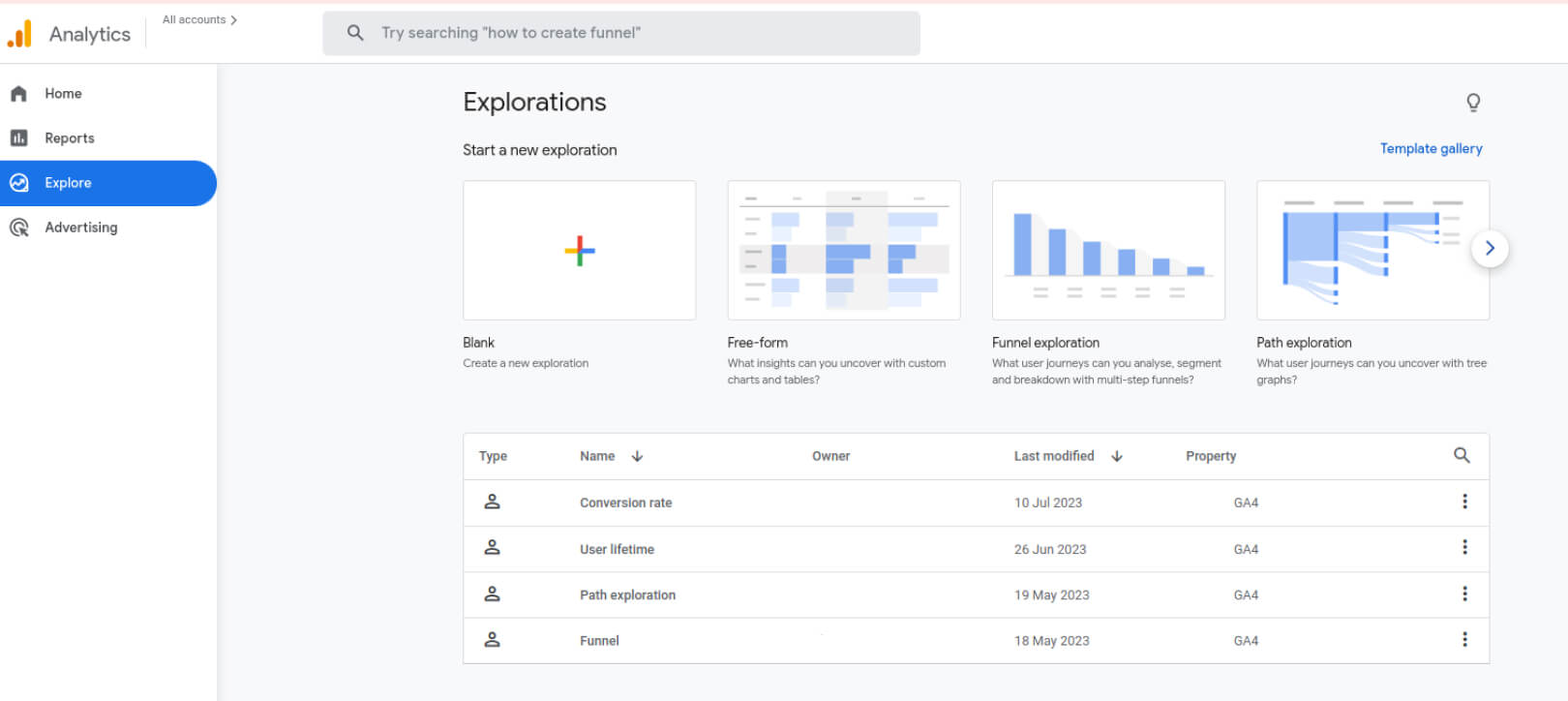
GA4 Explorations Dashboard
GA4 offers more sophisticated insights compared to UA. Thanks to the anomaly detectors it provides more detailed statistics on various aspects like unusually high user traffic or slow-loading web pages. You can find anomaly detectors when creating explorations in GA4.
Custom Alerts
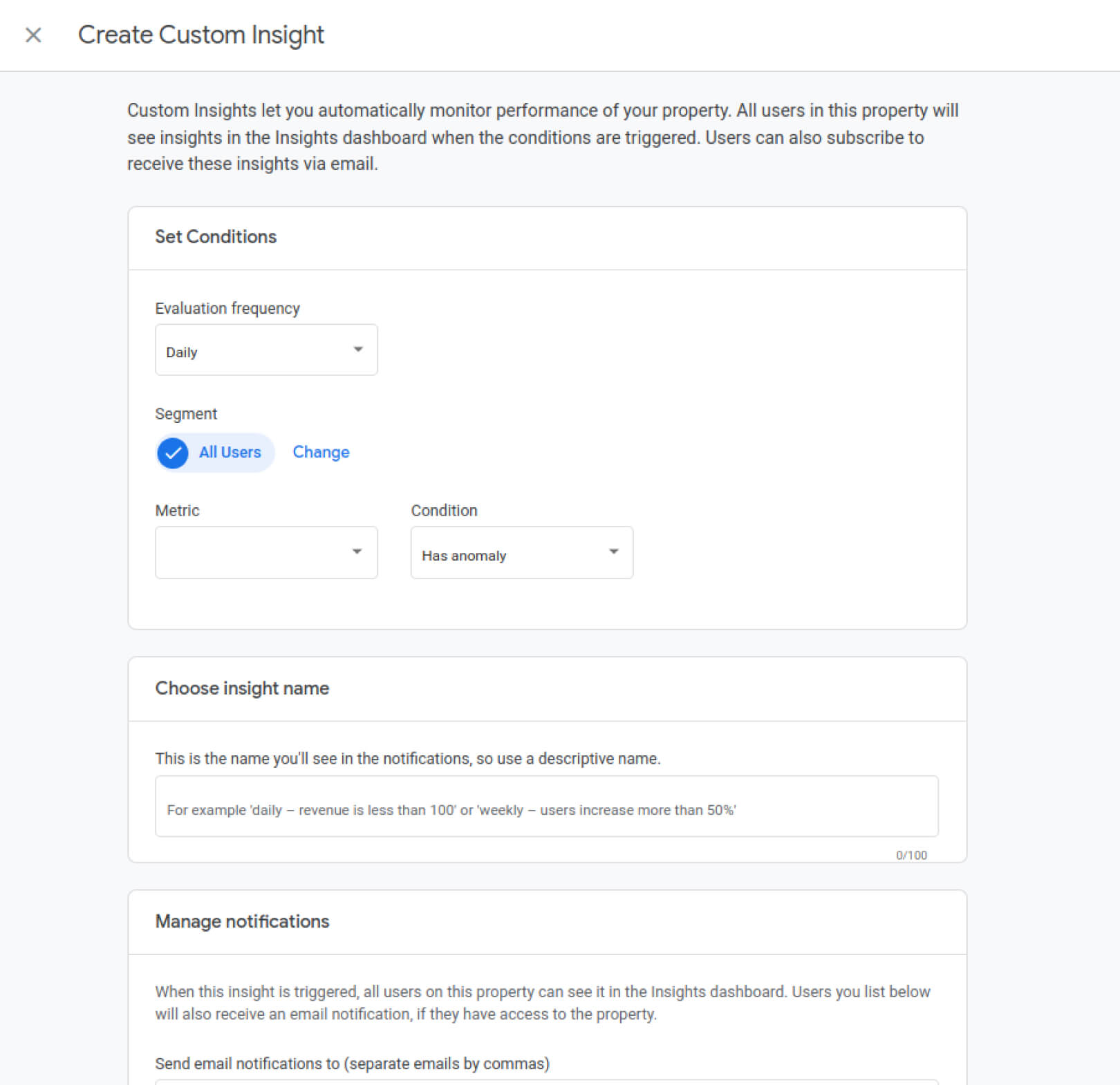
When looking at GA4 vs. Universal Analytics, custom alerts in GA4 are improved. For example you can receive an email in different situations such as sudden drop in conversions or unusual web traffic.
- GA4 offers suggested custom insights/alerts that users can select automatically.
- GA4 allows creating custom rules for insights from scratch, tailored to individual needs.
- The path to creating custom insights: scroll down to GA4’s default homepage -> Look for the section “Insights and recommendations” -> Click on “See suggested insights”
Predictive Metrics
Currently GA4 offers three predictive metrics:
- Churn Probability. The probability of active users becoming inactive within the next seven days, allowing businesses to proactively address customer retention strategies.
- Purchase Probability. The probability of active users making a purchase within the upcoming seven days. This metric helps businesses understand and optimize their marketing efforts to target users who are more likely to convert and make a purchase, maximizing their sales potential.
- Predicted Revenue. Assist in budget planning by forecasting active user numbers for the next 28 days.
Predictive Audiences
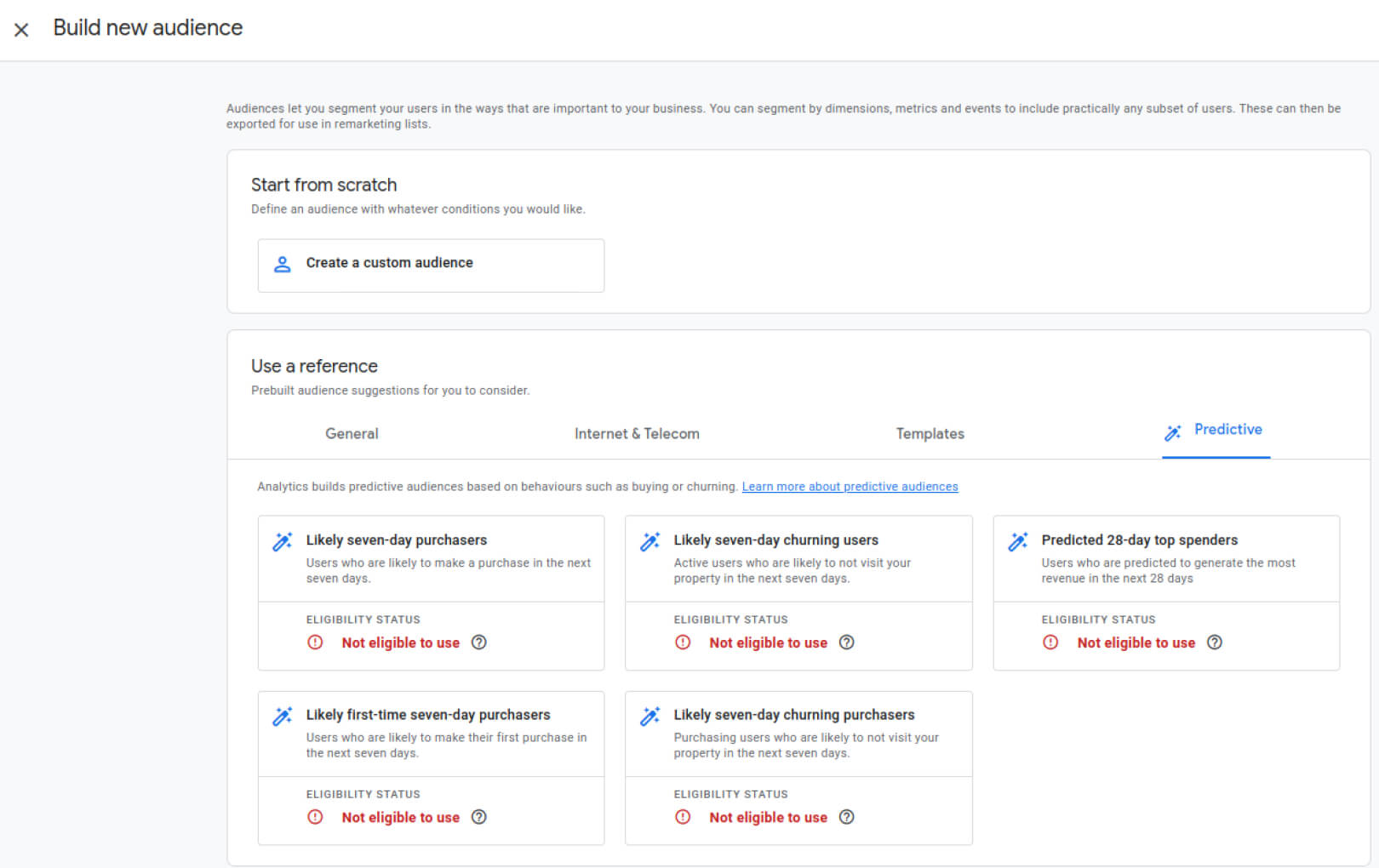
When used together predictive metrics and predictive audiences can be an effective combination. However there are minimum requirements. You need at least 1000 positive (purchases) and 1000 negative (non-purchases) in the last seven days. If you don’t meet these criteria, the Predictive Audiences are marked with “Not eligible to use”.
- Pre-built audiences. GA4 provides pre-built audiences like “Likely seven-day churning purchasers”.
- Create custom audiences. You can combine predictive metrics and other behavioral data to create custom audiences.
- Audiences can be shared with other Google products. In GA4, you have the capability to share your audiences with other Google products like Google Ads. For example, you can create a churn audience and subsequently target those users with an ad campaign.
GA4’s dashboard for creating a new audience
Behavioral Modeling
Behavior modeling in GA4 offers significant benefits by leveraging machine learning to predict user behavior, detect anomalies, and create predictive audiences.
But it also brings challenges. In some regions of the world, privacy laws mandate user consent for tracking purposes. To address this, GA4 introduces Consent Mode, which utilizes anonymous pings to fill data gaps and model the behavior of users who haven’t provided consent.
Wrap Up
In the future, Google is expected to enhance GA4 by offering additional predictive metrics and improving recommendations. Free users will gain the capability to utilize raw data in BigQuery, unlocking opportunities for data scientists to delve into and develop custom features.
Love it or hate it, It’s clear that GA4 represents a significant advancement in web analytics, empowering businesses to be able to make insightful and data-driven decisions in the evolving digital landscape. Now go and get it!




