For a business to flourish and make a profit, its products and services need to be the foundation of its success and be well-accepted and appreciated by the target audience. In other words, there has to be market demand for them.
The customer’s needs can be identified through various methods of market research, and those should be used to make your value proposition not only meet but exceed people’s expectations.
However, in a competitive marketplace, as there is rarely a single provider that supplies a product, the customer may choose a different company over yours.
That’s why marketing and branding are so important. By analyzing and understanding market demand, your marketing strategy can ensure that your products will see commercial success.
In this article, we’ll tell you about everything you need to know about market demand, how to leverage it, and how to try to influence it.
What Is Market Demand?

Simply put, market demand is the touchpoint between the client’s willingness and ability to buy a product. It should not be mistaken with the customer’s needs and desires. A person may need a product or service, know where to find it, and want to buy it, but be unable to afford it.
When estimating demand, and while companies research needs and wants because of potential future market expansion, the focus should be on the customers who are able to afford the product and are willing to pay the price.
Understanding payment limit, budget, frequency of purchase, and buying volume, as well as the overall number of potential clients enables a company to estimate market demand.
Demand can be measured three ways:
- Individual Demand – for a single household/business.
- Market Demand – for a target market.
- General Demandor – for the whole economy.
Most companies usually focus on individual demand and market demand. However, depending on the type of product and investment, fluctuations in general demand should also be taken into account.
What Is a Market Demand Curve?
Demand is usually visualised as a line or curve on a line graph, where the Y-axis is the price of the product, and the X-axis is the quantity consumers buy.
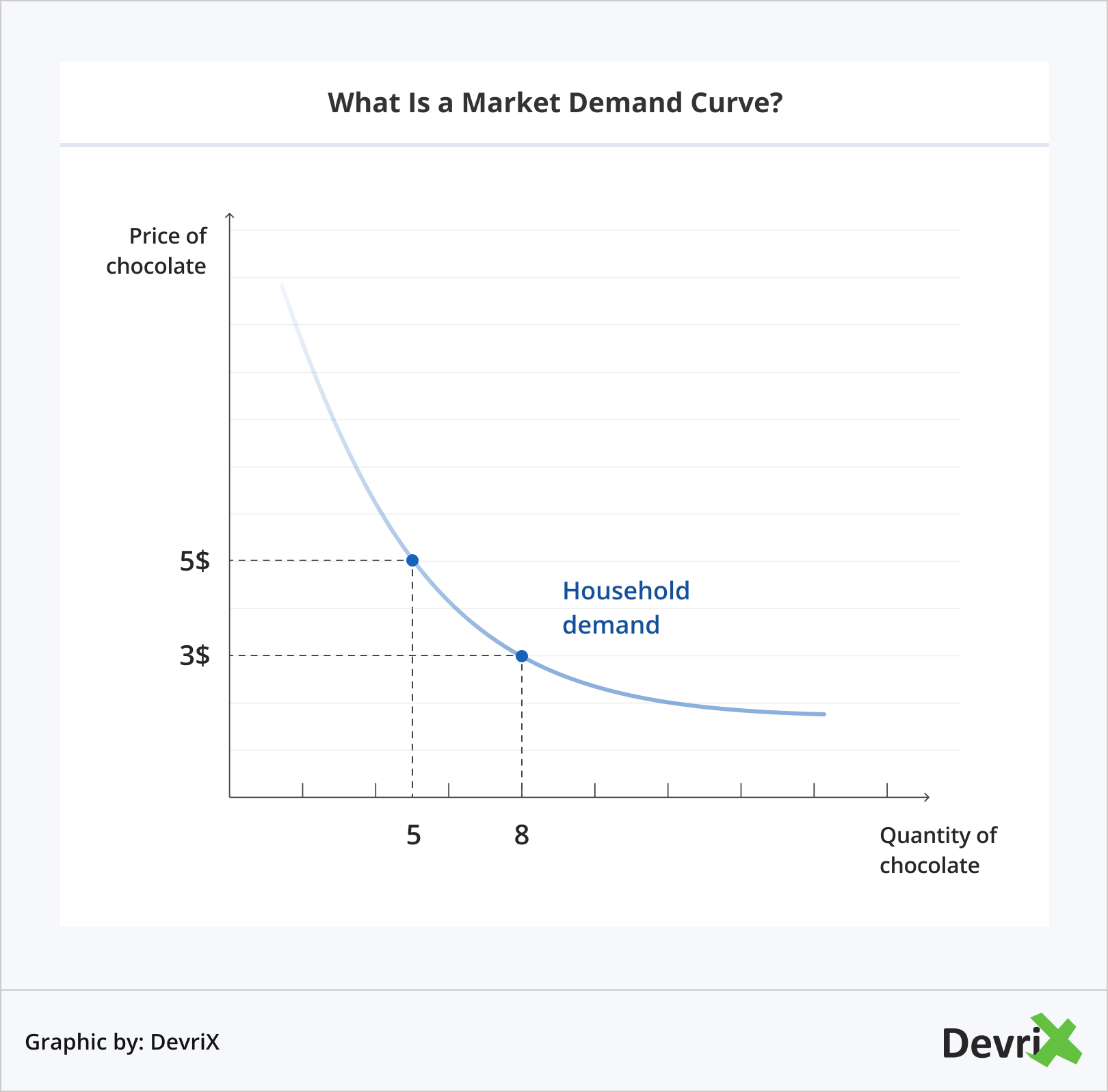
Generally, the price and the quantity are not constant – if the price increases, the quantity people are willing to buy decreases, or the other way around. If you move the price point-position on the Y-axis, you can easily find how the quantity will also become different. By changing the values, you can see how market demand fluctuates.
However, the curve is not affected only by the price. It can be influenced by things such as scarcity, popularity, branding, etc. These can make practically any price within the customer’s budget acceptable. Nevertheless, as the price rises, the business is bound to losing clients who were already at their limits when the price was lower.
In a competitive market, supply and demand are interconnected and self-regulate, they create the so-called market equilibrium. Shifts in the demand affect the market equilibrium and the need for supply. Understanding this can provide businesses with an insight into the processes behind market demand, and enable them to use it in their marketing strategy.
How to Calculate Market Demand
First of all, it should be pointed out that calculating market demand is based on hypothetical behaviour and should always be taken with a pinch of salt.
That said, to calculate market demand, you should find out if there is interest in your product and how many people are willing and able to pay the price. This can be accomplished by distributing surveys, monitoring social media platforms, researching industry trends, and etc.
Once you’ve identified your target market, choose a sample that represents your customer segments, and test how their purchase behavior would change with the change of the variables.
The sample should be large enough to be representative of the whole market and include customers with various levels of interest in the product. Otherwise, you risk the results being too narrow or inaccurate.
To calculate market demand for the whole segment, you should calculate and add up the individual demands for each household/business.
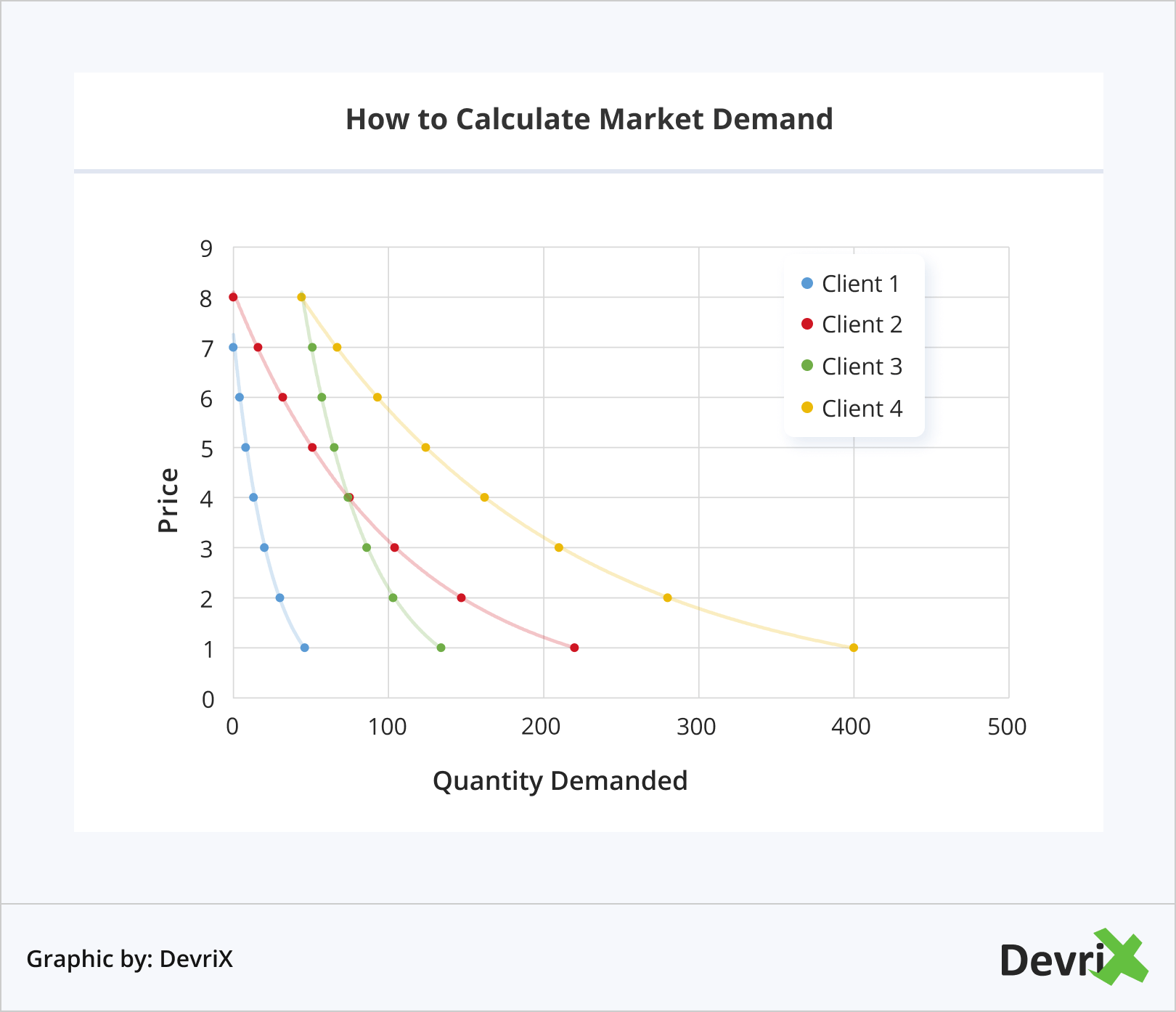
The formula for individual demand is:
Qd = a – b(P)
Where “Qd” stands for quantity demand, “a” represents the factors affecting price other than price itself, such as the customer’s income, budget, ect., “b” is the slope of the demand curve, and “P” is the price of the product.
You can find detailed information on how to calculate individual market demand here and here.
Researching and Analyzing Market Demand for Marketing Purposes
As mentioned, market demand can be estimated using surveys and social media listening tools. However, companies that want to leverage it should obtain a deeper understanding of their customer’s buying behavior.
They can rely both on secondary and primary research methods, especially when the business is planning large investments and wants to evaluate the product/market expansion risk.
Build Customer Profiles
Studying demand starts with understanding who your customers are, why they need the product, what they love about it, etc.
Aside from being a cornerstone of sales and marketing, client profiles enable you to analyze how well penetrated the market is and whether there is potential for increasing demand.
For example, if the market segments that benefit the most from your product are already engaged, you may be close to saturating the market. Depending on the product, this may mean that you should:
- Focus on retention and boosting sales volume.
- Find a way to further develop your product (introduce new features, create supplementary products, create an ecosystem business model, etc).
- Find a new market.
Understanding your customer’s purchase behavior and demand motivation is essential to understanding and mastering demand. Otherwise, you risk basing decisions on data that is not relevant.
Conduct Pricing Research

Pricing research is a major factor in studying market demand. Although the customer might be willing to pay the price if it’s too high, they simply won’t because the cost is above their budget.
The product’s price elasticity is also a major factor. Elasticity is the price’s ability to fluctuate, without causing losses or making the price too high for the market to sustain. Also, some products may have relatively flat prices which makes it difficult to control their demand.
Furthermore, competitor pricing should also be taken into account. If you charge too much, there is almost no way to convince the customer to buy your product instead of a similar one that provides relatively the same benefits but at a better price.
Invest in PESTEL Analysis
To ensure the utmost accuracy, demand research should include a PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental and Legal) analysis. Without considering the consumer environment, even the most detailed market demand estimations can be flawed.
That’s because the desire and ability to buy are strongly affected by external, and often unforeseen, factors. And although these can’t always be accurately foreseen, nowadays predictive analytics is advanced enough to provide valuable insights.
PESTEL analysis is complicated to conduct and therefore, left out or overlooked. However, depending on your investment, market trends, and so forth, it may make all the difference.
For example, in a recession, customers are less likely to buy expensive things, and products that are not imperative, and at the same time remain more loyal to brands they know. Therefore, if you are looking to penetrate a new market with a luxurious product, your chances of success will be questionable at the least. However, if you only rely on past data and don’t consider the present and upcoming trends, you may not see the recession coming and suffer major losses.
Monitoring the economic climate and checking out relevant industry grade secondary research will enable you to better plan your investments, and understand the market’s demand potential.
Managing Market Demand With Marketing Strategies
Depending on the stage of development of your product, the market, and the industry, there are different ways to effect and manage market demand.
Demand Creation

Demand creation is vital to new product development, especially if the customer is not familiar with it, or the company is looking to enter new markets.
When this happens, market demand is not a given. You have to first educate the customer about the product, convince them that they need it, and that they want it. In other words, you have to create demand.
In order to do this, you should start with the research methods we’ve talked about, and understand how to approach your audience. Your goal is to study their profiles, behavior, and needs, and find out how they can benefit from the product.
In addition, consider performing voice of the customer research, creating customer journey maps, and filling out a value proposition canvas. These will enable you to build a holistic image of your clients, and understand them. Your focus should be on their needs, what motivates their willingness to make a purchase, and what their ability to buy is dependent on.
Once you know your customer well, you can launch personalized push and pull marketing campaigns to introduce them to products and showcase how they can benefit from them. Your overall goal is to build a strong value proposition, inform, and educate.
Furthermore, when it comes to novelty, you should strive to create a buzz around the product and encourage early adopters with promotions and offers. This segment can later on become a powerful tool in your marketing strategy, and should be nurtured to contribute with reviews, user-generated content, positive word of mouth, and other forms of customer advocacy.
Demand Generation
When your product is already familiar to the customer, there are various ways to affect market demand.
The main goal of demand generation is to introduce new audiences to your product and expand your market, or convince existing customers to increase their purchase activity. To that end, you can either address the customer’s willingness to buy, or their ability to afford the product.
- Increase Willingness to Buy. By researching your existing audience and potential segments, you can find new ways that they can benefit from your product and use them as selling points. You can also improve and personalize your marketing message to better respond to the customer’s needs, pain points, and desires.Once you’ve identified how to approach the market, you can launch brand awareness campaigns, co-marketing initiatives, promote new features, and encourage customer advocacy.
- Affect Ability to Buy. As mentioned, price fluctuations play a major part in market demand. More often than not, for every product there is a customer segment that is more than willing to buy it but simply can’t afford it. Researching their budgets and spending limits and cross-referencing the information with your product’s price elasticity will enable you to regulate how much you charge.Combined with the right marketing message and the proper campaign, this will give you access to an expanded market, and will enable you to increase demand.Furthermore, you can also consider implementing dynamic pricing campaigns that provide more value to the customer and may convince them to buy. These can include seasonal discounts, bundle offers, loyalty programs, and more.
Bottom Line
Understanding and managing market demand are essential to a business’s success. Even the greatest product will flop if people don’t want, need it, or if they can’t afford it.
With modern technology, analysing market demand is easier than ever before. However, although it provides almost limitless opportunities to observe and engage the customer, the digital environment also creates challenges. People have access to more information and more choices than ever before, and their behavior may sometimes be difficult to understand and predict.
Before entrepreneurs make an investment or start a new endeavor, they should research market demand, and make an effort to understand their customers. Furthermore, they should take into account the dynamic economic climate and technological advancement.
The best way for companies to stay ahead of market demand is to maintain active communication with their clients and monitor for behavior changes. They should also build resilience and be ready to adopt new digital business models, evolve with the market’s needs, and learn to ride the demand curve, instead of fighting it.




