Backlink auditing is the first step to evaluating your link-building strategy and an essential practice for any webmaster and SEO professional. Backlinks are one of the top three most important Google ranking factors, and with over 5 billion searches happening in one day you need to be cautious about who links back to you. So, if you want your website to reach the SERPs of many you need to be aware of how you can help it rank higher.
When conducting a backlink audit you are essentially evaluating every link that points back to your website and then designing a strategy to manage them better. There’re various ways to review your links. You can do it manually by downloading your list of links with the help of Google Webmaster tools and then going over each one individually. Or you can use a tool to do it automatically. Your choice will depend on the size and scale of your website – the bigger it is the more time the backlink audit will take.
A thorough link audit can help you discover potentially risky links and improve your SEO strategy. Quality links will indicate to Google that your website has authority and that it can be trusted. This will help you create a better user experience, improve your page traffic and limit the possibility of a PageRank penalty, thus making your website more popular in the Google search engine.
Because we understand the importance of strong backlinks, in this article, we have prepared a six-step guide to backlink auditing. We will be explaining why backlinks are important, how to prepare for and then conduct a backlink audit, and share with you a few tools that you can use in the process.
What Are Backlinks and Why Are They Important?
Backlinks, also known as inbound links or external links, are any type of links that take a user from one webpage to another. These are links from third-party sources that lead to your website, which is different from internal links that connect two pages within the same website.
In other words, they are outside links that point to your website that don’t always come in the form of text but can be images, videos, graphics, etc.
Alongside content, backlinks are a crucial ranking factor Google’s crawlers will index your website and as such, the backlinks become an important part of Google’s ranking algorithm. According to MonsterInsights, they go hand-in-hand with content because they help in generating organic traffic.
Backlinks evaluate the trustworthiness of both your website and your domain. They propose votes of confidence for your page that Google uses to estimate if you deserve to rank in the top search results.
From an SEO perspective, this means that the more trustworthy your links are the faster your page will be indexed and ranked.
The Main Types of Backlinks
All that said, because not all backlinks are the same, here are the different types you should know about.
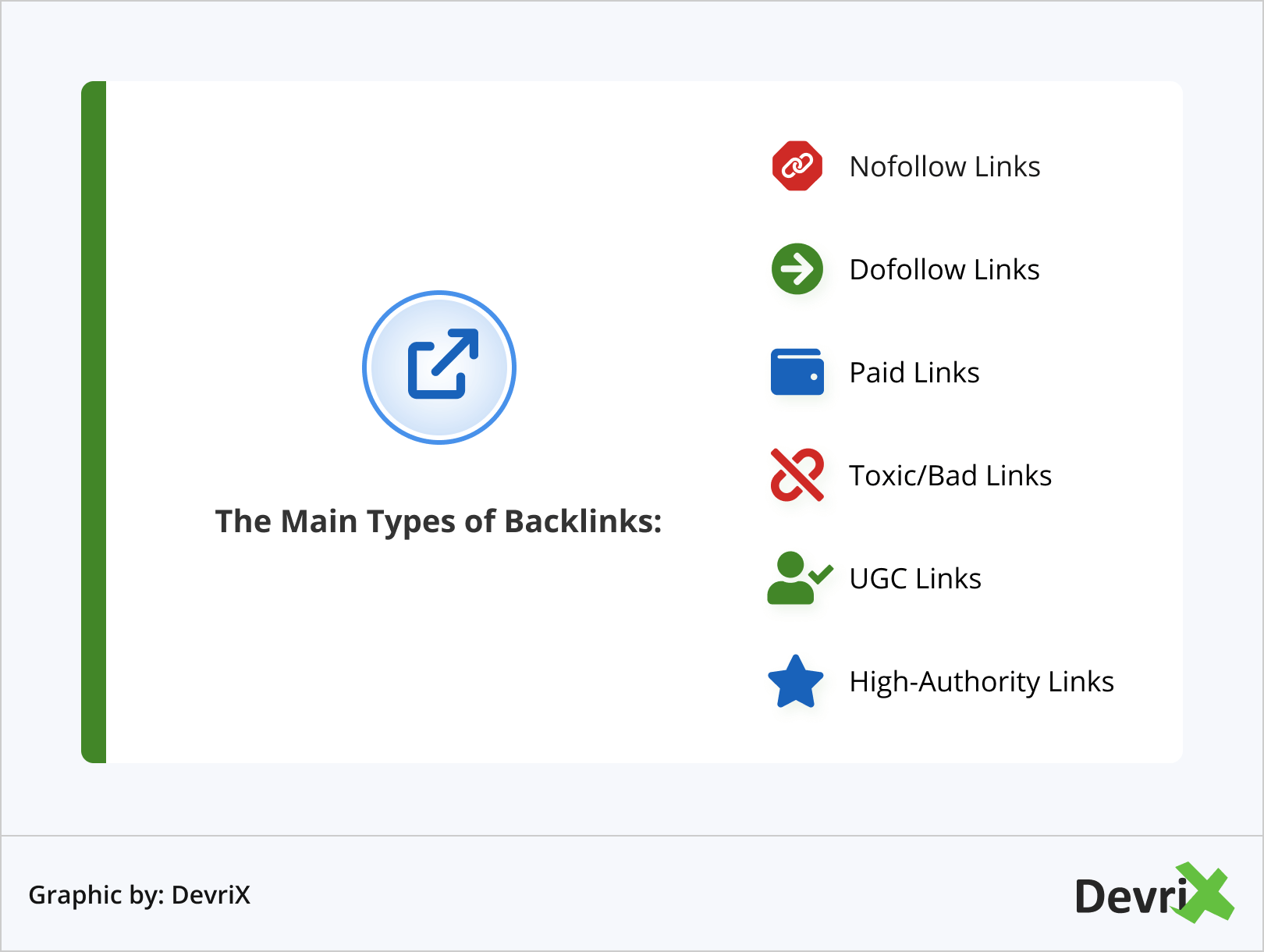
1. Nofollow and Dofollow Links
Nofollow links are links that include a rel=“nofollow” attribute to the <a> tag that tell search engine crawlers to ignore the link when estimating page rankings.
They were invented so that spammy links from comments or user-generated content don’t affect the overall webpage rankings. However, they don’t pass Google’s Webmaster Guidelines which means they won’t help you rank any higher.
Google used to not count any link that had the nofollow tag in it, but since September 2019 they’ve changed their algorithm and now treat all link attributes as only suggestions that could be excluded or included. This means that in some cases nofollow links are excluded by crawlers and in others, they’re not.
Do follow links are thus links that pass Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and don’t have a nofollow tag.
2. Paid Links
These are links that a third party is paid to share. The payment can be monetary or exchange of products/services.
Google understands that paid links are naturally used for advertising, and when that’s the case they should be designated as such, either by adding a nofollow tag or by redirecting the user to an intermediate page that is blocked from search engines.
However, there are paid links that are not used for advertising, but rather for manipulating PageRank. Selling or buying such links violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines, making it a risky link-building tactic that can negatively impact your page’s rankings.
3. UGC Links
As the name suggests, these are links that come from user-generated content (UGC) – i.e. shares, likes, comments, reviews, etc.
Having your users share their impressions of your webpage is generally a good thing, but if UGC links turn into spam they can affect Google’s assessment.
The good thing is you can reduce the chances of this happening by adding spam-blocking attributes like rel=”nofollow” or rel=”ugc”, moderating comments, using anti-spam tools and techniques, and more.
4. Toxic Links
Also known as unnatural or bad links, toxic links come from suspicious or low-quality sites that can harm both your current and overall ranking.
These are intended to manipulate search engines’ assessment of your site, and also violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
5. High-Authority Links
These are links that come from certified trusted sources such as newspaper outlets like the Guardian and New York Times, well-known business news sites like Forbes and Inc., and any other established website that has earned trust.
Now that we’ve briefly established the backlinks basics, let’s learn how to analyze and manage your site’s outbound links effectively.
The 6 Must-Follow Steps to Backlink Auditing
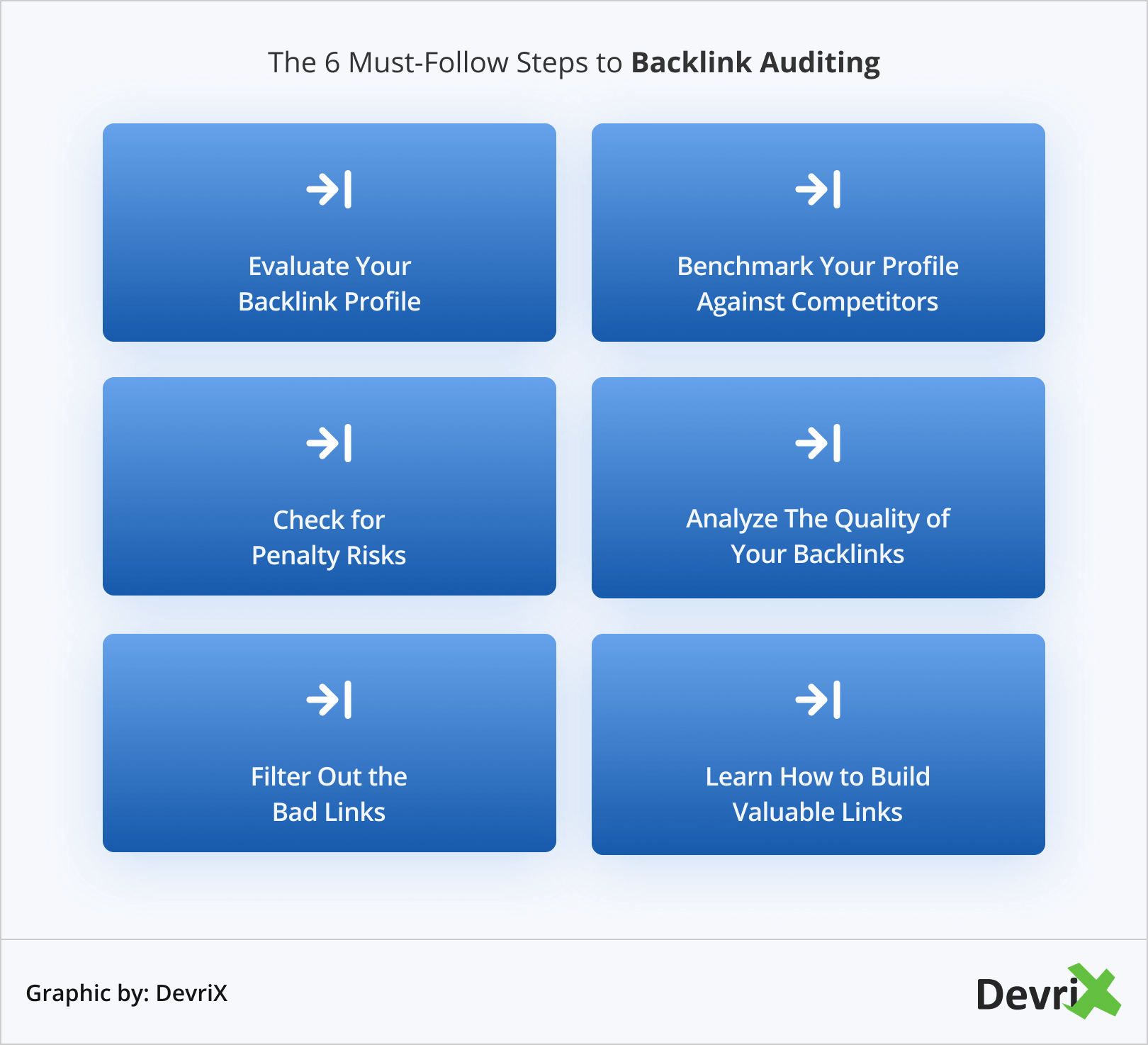
1. Evaluate Your Backlink Profile Carefully
The very first step to battling auditing is to construct a backlink profile, that is if you don’t have one already, and to analyze it carefully. This profile will tell you:
- How many external links your site has.
- Which pages of yours have the most links leading to them.
- Which websites link to yours more often.
- Which are the most common anchor texts used for the external links.
You can use the Google Search Console to create your backlink profile, and you can also use a dedicated tool.
After you have generated your backlink profile, it’s time to get some insights from it. Here’s a list of the most important things you should look at:
- Overall Toxic Score – This will indicate the number of harmful links pointing to your website. Too many toxic links can negatively impact your rank score.
- Number of Referring Domains – You should have a good balance of quality domains that refer back to your website. If too many links come from one domain it can make Google suspicious.
- Total Number of Analyzed Backlinks – If this number is low it can indicate that your site is perceived as harmful by others. Alternatively, if this number is high, but you’re not making any link-building efforts or publishing new content, it could mean that you’re exposed to a spam attack.
- Trends in Gained or Lost Backlinks – The logic here is similar to the one in the previous metric: a spike of lost links can negatively impact your rankings, and a spike in gained links can be both a good and a bad thing depending on the amount of link-building efforts you put in.
- Toxic Score of Referring Domains – If this color is high it can indicate poor link-building practices.
- Percentage of UGC Links and Nofollow Links – These links are generally ignored when search engines make their estimations, so naturally, you shouldn’t have a high proportion of them.
This first step is the foundation of a good backlink audit, so take your time with it. The better you know how your backlinks are performing in searches, the more effective your efforts will be for improving it.
2. Take a Look at Your Competitors’ Backlinks
After you have analyzed your link profile it’s time to take a look at what your competitors are doing. Since backlinks are a key search engine ranking factor it will only benefit you to understand the link-building strategy of your competitors’ so you can better evaluate your own profile.
Here are some key metrics to look at:
- Number of Backlinks – These will help you understand your own link footprint so you can later benchmark it against your competitors.
- Authority Score – This corresponds to the attractiveness of the domain for link-building prospects.
- Backlink Type – This relates to the type of content that is linked to the most – text, image, graphics, forum, etc.
- Link Attributes – These will help you spot potential weaknesses.
- Referring Domains – With these, you can estimate if the number of domains a site is currently reaching out to is enough.
If you used Google Search Console in the first step of the audit, you should have a pretty good overview of your own external links. However, if you would like to get some insights on your competitors’ link profiles you would need a dedicated tool like Semrush, Ahrefs, or Moz, to help you achieve this.
Read also: How to Measure the ROI of Building Backlinks
3. Check for Penalty Risks
Before you conduct a backlink analysis, it’s important to make sure that you don’t have any penalized links.
There are two types of link penalties – manual and algorithmic.
Manual Penalty – This type of penalty happens when a member of Google’s team reviews your link and finds something wrong with it. This review could be triggered by an error found in your link profile after Google’s algorithmic review, a spam report by a competitive website if you were in a highly competitive niche that Google monitors actively, or if you just have bad luck. If you have been penalized manually you will receive a notification in Google Search Console.
Algorithmic Penalty – This is a penalty that is automatically applied by Google depending on your link profile’s end. It does not require a human review. A large part of algorithmic penalties is triggered by Google Penguin. If you have been penalized algorithmically you will not receive a notification. But you will notice if your organic traffic starts going down really fast.
Both of these penalties will negatively affect your ranking and will often result in decreasing the inbound traffic to your site. So it’s highly necessary to make sure you check for any notifications or dramatic drops in traffic and analyze if that’s happened due to a penalty. A good rule of thumb to avoid getting penalized is securing more organic backlinks.
Read also: Why Your Backlinks Aren’t Being Indexed?
4. Analyze the Quality of Your Backlinks
Now that you have a detailed perspective of your own backlink profile, and you have looked at how your competitors are performing, make an overview of these 4 key backlink-building attributes.
- Domain Authority and Relevance – The domain authority and topic relevance of your backlinks, will help you see how successful you are in finding and securing favorable backlinking opportunities. The higher the authority score and the more unique your referring domain is the better ranking you’ll have.
- Anchors – Keep an eye on anchor texts, pages, and link attributes. Take an account of which are the most common link anchors across your backlink profile. Evaluate how they perform and which keywords they rank for to ensure that all your backlinking features will be of interest to your audience.
- Spot Where Most of Your Backlinks Are – Identify which pages earn the most external links and try to understand why they perform better.
- Know the Types of Backlinks – Try to really understand the difference between the most important link types and make the necessary adjustments to ensure you don’t run the risk of losing your page rank.
After you’ve made an overview of your backlinking strengths, let’s go on to eliminate any weaknesses.
5. Filter Out the Bad Links
When creating or improving your link-building strategy it’s important to focus on quality over quantity. Low-quality links can greatly harm your organic traffic and rankings. Toxic links or unnatural links are used to manipulate PageRank and are considered a violation of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
A long time ago using links to manipulate webmaster guidelines was a common practice for improving website rankings. Luckily search engine algorithms have improved since then and now make considerable efforts to encourage white-hat SEO practices.
But What Kind of Links are Considered Manipulative?
Manipulative or toxic are any bad and very low-quality links that aim to trick a website’s ranking in Google. These could be coming from spammy sites, forced into blog comments, hidden in a web page’s footer, or placed at exact match anchor text. They are very harmful to your search rankings, so it’s kind of obvious that you should get rid of them.
This can be done in two ways – by removing or disavowing them.
- Removing a Toxic Link means contacting the owner of the referring website and asking them to delete the link. You will often need to prove you’re not a Spambot. It is also a good practice to make sure you are polite when asking.
- Disavowing a Link means adding it into the Disavow list, after which you export it to Google Disavow tool. Keep in mind that Google treats disavowing as a last resort option. This means that you must prove that you’ve done everything you possibly can to remove the link but that all those efforts fell short. Moreover, you will need to document all the steps that you have taken and then present them to google as evidence so that they can start the disavow procedure.
The point is not to waste time trying to contact scammers or spammers but to actually separate toxic links from those that can be removed and others that can’t.
6. Learn How to Build Valuable Backlinks
We have talked plenty about removing threats from your backlinks portfolio, and while this is a core purpose of the backlink audit, so is helping you find new opportunities to improve your overall link-building strategy.
Here are a few tips to consider:
- Always keep a close eye on your backlink profile so you don’t miss out on any important changes.
- Focus on the reputable domain links in your profile. Make sure to add them to your outreach list. Google uses these as a vote of confidence that websites are trustworthy and authoritative.
- Connect your Google Search Console and your Google Analytics profiles. This will give you an even more comprehensive view of how different things are performing on different pages of yours and which get the most referral traffic.
- Analyze your anchor texts. Ensure that they provide relevant information about the content that it’s linked to. Keep them short and straight to the point, use keywords with a lower density, and avoid using generic words.
- Compare your backlink profile to at least five competitors. Make sure you evaluate both the strengths and weaknesses of each one.
To obtain overall powerful insights from your backlink audit, consider it as a Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis of your backlinks. At the end of the day, it should help you not only gain better rankings but overall improve your SEO strategy and provide your audience with quality experiences.
Conclusion
Backlinks are the second most important search engine ranking factor after content, so you should take them seriously. They act as a vote of confidence by indicating that your web page is a credible and trustworthy outlet for information.
Quality overrules quantity and Google knows it. When authoritative websites with authoritative domains link back to your site, Google will be happy to rank it higher in SERPs, thus qualifying it as a high authority site as well.
Furthermore, a backlinks audit shows both the good and the bad side of your link-building strategy so you can improve it. That’s why you need to make sure you pay attention to the details and continuously evaluate the current state of your link profile.




