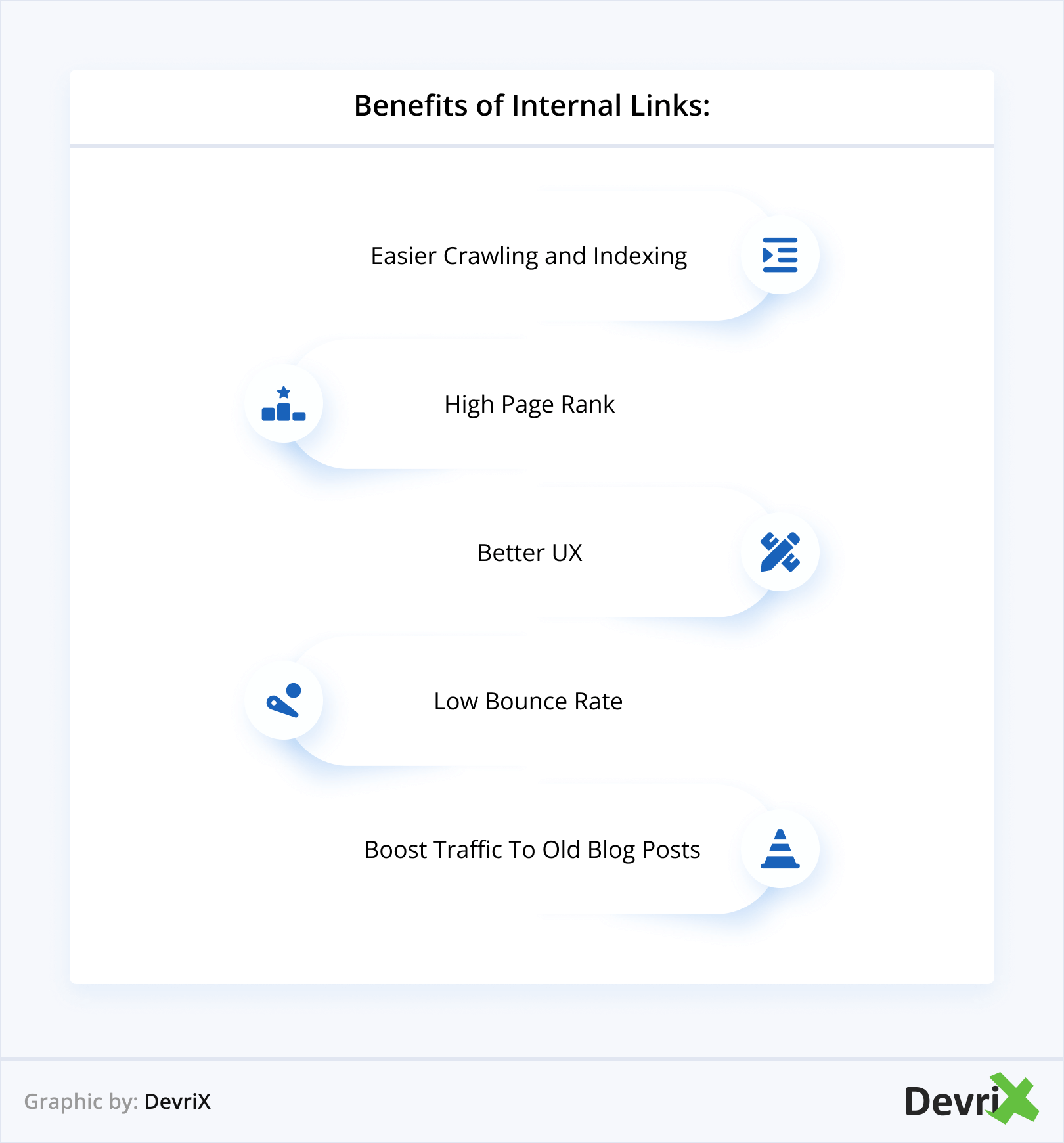
Without links, it’s impossible to rank your content! With a proper internal linking strategy, you can connect the related pages on your site, showcase your best content, and help Google discover your best posts and pages.
Internal links provide Google with the structure of your website. They also determine the hierarchy of your site, allowing you to give more value to certain pages and links on your site. With the right internal linking strategy, you can boost your SEO and improve the usability of your website as well!
However, just merely inserting links into your content will not deliver the SEO and usability gains that you’re looking for. For that reason, here are some practices that will improve your internal linking, along with bad habits that you need to avoid.
Understand the Importance of Internal Links
Google uses internal links to help discover new content. Internal links are excellent if you want to show Google the most relevant pages on your website, or the pages that you most frequently link to.
If you publish a new page and don’t link to it from another page on your site that isn’t included in your sitemap, then Google’s web crawler can’t locate it:
“Google must constantly search for new pages and add them to its list of known pages. Some pages are known because Google has already crawled them before. Other pages are discovered when Google follows a link from a known page to a new page.”
Internal links also help increase the PageRank of your site. The more internal links a page has, the better its PageRank.
Internal linking is also extremely important for SEO. That is because there are pages on the Internet that you can only access through internal links.
It can help you rank your internal pages better, even if you lack external links. This matters especially for long-tail search queries, where you can achieve a better ranking with contextually-appropriate subpages.
Internal linking is also beneficial to the user-friendliness of your website. The links help users navigate your website. So, in essence, internal linking is relevant for both SEO and the UX of your site.
Don’t Go Overboard with Internal Links
The more irrelevant links you include in your pages, the less link juice the links will send to the page they lead to. Furthermore, too many links can send spam signals to search engines. To analyze the internal link structure, you can use the Link Extractor tool.
Google’s instructions are clear:
“Limit the links on a given page to a reasonable number.”
So, what would be the right number of links that you can include on a site and not go overboard in the process?
Experts attempted to provide an answer, but even Matt Cutts doesn’t have a specific number:
“It seemed about right to recommend 100 links or so, and in some cases, it might make sense to have more than a hundred links.”
Even Yoast has a similar answer, tool:
“Well, how many links per page is always a weird question. As long as your links are useful for your users, it’s okay. There used to be a rule of no more than 100 links on a page in the Google Webmaster Guidelines; they’ve removed that rule. 100 links might seem like a lot if your site is a content site. But if you look at very long Wikipedia articles, they might have 300-400 URLs in there, linking to other articles and all those links are useful. So, if your links are useful like that, by all means, have them on the page.”
Keep in mind that the “magical” number of 100 links includes all the links on a given page. There’s not a definite number. Still, you need to pay attention to the user experience and include only those that are important.
Keep a Good Linking Structure
Google puts a lot of emphasis on links and their effect on web usability. For that reason, you shouldn’t ignore the importance of the linking structure. The link structure of your website must be as simple as possible so that users can navigate with ease.
You shouldn’t place too many internal links on one page or mark those pages as “HTML sitemap” in the robots meta tag. Having more than several hundred links on a page can make the job of following each link difficult for search engines.
You need to also put a limit to the number of internal links because too many links can confuse users. Instead, you should only place relevant and useful links that add value.
Siloing Your Links
You need to have a thematically appropriate linking on your website, which is also called siloing. Look at your website as a pyramid. The most important content is placed at the top and the least important content is placed towards the bottom.
Usually, at the top of the pyramid should be your homepage. Under the homepage, you typically have—About us, services, products, blog, and so on.
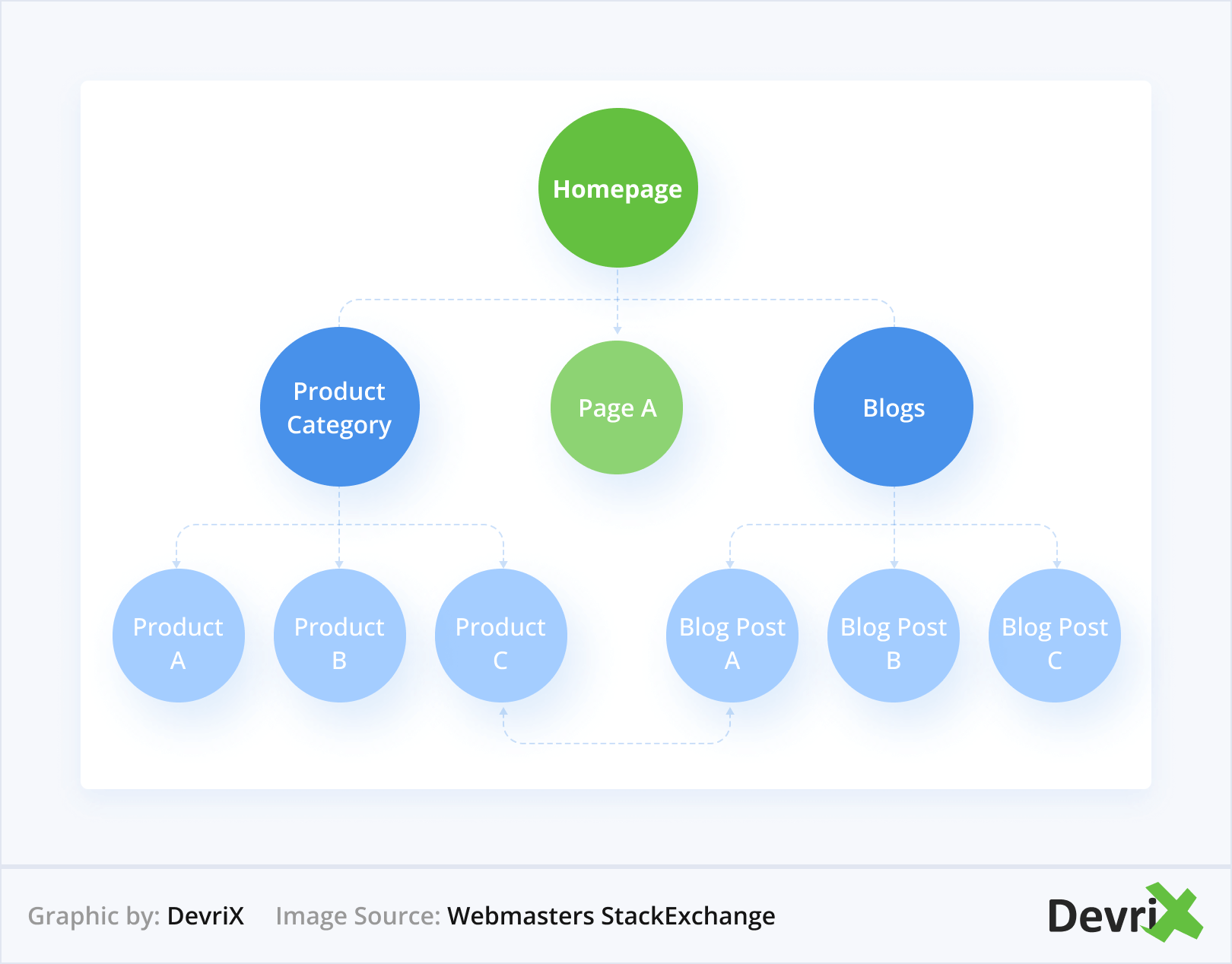
A silo structure for your content reduces the Google Sandbox time that your website undergoes after launching. By having pages structured in a silo, you also help Google gauge your topic relevance and increase your content semantics.
You also shouldn’t fill the navigation bar with too many links. If your website is too large, that would be confusing for the users. Since the navigation bar is there to help the users navigate on your site you should confine it to the only necessary links.
Keep in mind that you need to structure internal links in a manner that guarantees an SEO friendly website architecture. Each page should refer to relevant pages or the crucial areas of your website. That leads to higher internal link popularity of the main pages.
Don’t Leave Broken Links Behind
Having broken links on your WordPress website is terrible for both visitors and your site’s SEO. If users click on one of your links, it’s because they’re interested in learning more. By having broken links you discourage users from browsing your site further. Also, you risk a broken links penalty from Google.
Furthermore, broken links also diminish your site’s crawlability. Each 404 page that a Googlebot is confronted with is a page that could have been crawled. If you have broken internal links that should’ve led from one blog post to another, you’re losing the SEO benefits of that internal link.
There are several ways to uncover and fix broken links. One of the quickest methods is to use the W3C Link Checker, a free tool that examines your website for broken links and more. When you find the broken links with the W3C Checker, you have three ways to resolve them:
- Correct the Link: Perhaps you’ve entered an incorrectly spelled link. All you have to do is edit the broken URL and write the correct one.
- Replace the Link: Sometimes, it is better to replace the broken link with a functional one.
- Unlink: If the page that you linked to doesn’t exist or it’s no longer relevant, then it is better to remove the link from the page.
Additionally, you can use Semrush to check the status of your links, through the Site Audit report:
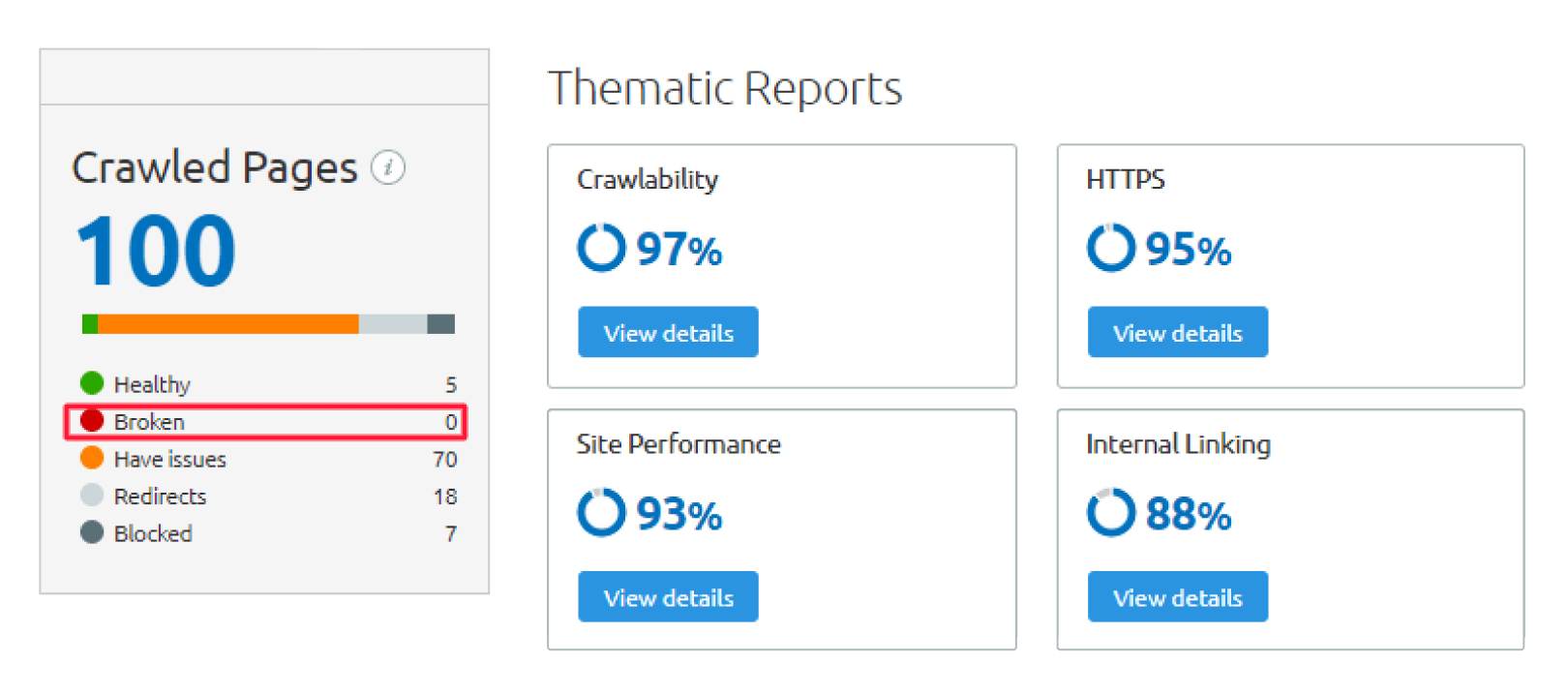
Fixing broken links will result in a better UX and increased web traffic, and ultimately, a better conversion rate for your company.
Use Keyword-Rich Anchor Text
Once you have decided on the internal links and which pages should acquire link equity, it’s important to use the appropriate anchor text. The anchor text is the clickable link text that visitors see on your pages.
Search engines use external anchor text as an indicator of how users view your link and what the page is about. You can use several types of anchor text:
- Exact-match: Anchor text is an “exact match” if it has a keyword that reflects the page that is being linked to. For example: ‘SEO’ linking to a page about SEO.
- Partial-match: These types of anchor texts include an alternate keyword on the linked-to page. For example: ‘SEO strategies’ linking to an SEO-related page.
- Branded: A branded name or keyword utilized as an anchor text. For example: ‘DevriX’ linking to a page from our DevriX Services.
- Naked link: Just a URL that is used as an anchor ‘www.devrix.com’.
- Generic: A generic word or phrase as an anchor such as “Click here”.
- Images: Whenever you use an image as an internal link, Google will use the text in the image’s alt attribute as an anchor.
Keywords-reach anchor texts can be effective. However, you need to make sure that they are written properly.
Naturally-flowing content and an anchor text that doesn’t feel spammy are pivotal. If your content is good and the keywords in your internal anchor text are the proper ones, you’re good to go. Also, make sure that the anchor text fits naturally into your copy and that the keywords are not the same keywords in every anchor text.
If you stuff keywords, you’ll hurt the quality of your content and your search engine ranking. Make use of keyword variations, synonyms, and LSI keywords to improve your content value and help you rank for your target keywords.
Link Old Posts To New Posts And Vice Versa
A common SEO mistake when posting new content is linking to older posts but not the opposite. However, it’s important to also update your old content with internal links to newer, fresher articles. This way, you will create a good flow of authority for your company’s mission statement while also helping new content rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Therefore, if you are ever wondering how to improve the organic search performance of your older posts, figure out how you can update them with fresher internal links. Provided the content is still relevant, link to it from your newer blog posts. This way, someone who is new to your blog and hasn’t seen that content yet might find it. Don’t let articles lose traffic just because of their publish date or positioning – they may be at the bottom of your blog and still rank well!
Wrapping Up
Consistent internal linking can have a powerful impact on your website, and it’s something that shouldn’t be overlooked. You do need to have a natural hierarchical site structure though so that the internal links can follow suit.
Just like with every other SEO strategy, internal linking requires commitment and persistence. If you stay focused and plan your internal linking strategy right, your pages will rank better, and users can explore your content better in the process.




